How to: Get into a high plank position on the floor, hands planted under your shoulders, butt down (a). Engage your abs by pulling your belly button in towards your spine (b). Squeeze your left glute to lift your left leg two inches off the ground, keeping your leg straight (c). Tap your left leg out to the side, then back to starting position. Repeat, then switch legs (d).
Treatment options include physical therapy, back exercises, weight reduction, steroid injections (epidural steroids), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, rehabilitation and limited activity. All of these treatment options are aimed at relieving the inflammation in the back and irritation of nerve roots. Physicians usually recommend four to six weeks of conservative therapy before considering surgery.

Really great content. I also had some lower back problem but now that I know the source, I will work on it. My counsins also talked to me about this product called Panifix, or "Unlock your hip flexor" which Gives You A Practical, Easy-to-follow Program You Can Use To Instantly Release Your Hip Flexors For More Strength, Better Health And All Day Energy. Proven Swipes And Creatives Here:https://tinyurl.com/yd6nbzfh

Imaging is indicated when there are red flags, ongoing neurological symptoms that do not resolve, or ongoing or worsening pain.[5] In particular, early use of imaging (either MRI or CT) is recommended for suspected cancer, infection, or cauda equina syndrome.[5] MRI is slightly better than CT for identifying disc disease; the two technologies are equally useful for diagnosing spinal stenosis.[5] Only a few physical diagnostic tests are helpful.[5] The straight leg raise test is almost always positive in those with disc herniation.[5] Lumbar provocative discography may be useful to identify a specific disc causing pain in those with chronic high levels of low back pain.[41] Similarly, therapeutic procedures such as nerve blocks can be used to determine a specific source of pain.[5] Some evidence supports the use of facet joint injections, transforminal epidural injections and sacroilliac injections as diagnostic tests.[5] Most other physical tests, such as evaluating for scoliosis, muscle weakness or wasting, and impaired reflexes, are of little use.[5]

At the very least, the tension and/or spasm in muscles that cross over the hip and attach onto the pelvis can contribute to imbalance, in terms of how strong and flexible each muscle group is in relation to the others. But muscle imbalance in the hips and the spine may make for pain, limitation and/or posture problems. It can also increase the healing challenge put to you by an existing injury or condition, for example, scoliosis.
Epidural steroid injections are most commonly used in situations of radicular pain, which is a radiating pain that is transmitted away from the spine by an irritated spinal nerve. Irritation of a spinal nerve in the low back (lumbar radiculopathy) causes pain that goes down the leg. Epidural injections are also used to treat nerve compression in the neck (cervical spine), referred to as cervical radiculopathy, which causes pain.
Disc degeneration remains a key cause of chronic low back pain and the pain often persists despite surgery. NIH-funded basic science and preclinical studies are investigating molecular-level mechanisms that cause discs in the spine to degenerate, as well as protective mechanisms involved in disc remodeling that may diminish with advancing age. Such studies may help identify future therapeutic strategies to block degenerative mechanisms or promote remodeling processes. NIH also is funding early research on stem cell approaches to promote disc regeneration and rejuvenate cells of the nucleus pulposus, the jelly-like substance in the center of intervertebral discs that loses water content as people age.

Spinal manipulation and spinal mobilization are approaches in which professionally licensed specialists (doctors of chiropractic care) use their hands to mobilize, adjust, massage, or stimulate the spine and the surrounding tissues. Manipulation involves a rapid movement over which the individual has no control; mobilization involves slower adjustment movements. The techniques have been shown to provide small to moderate short-term benefits in people with chronic low back pain. Evidence supporting their use for acute or subacute low back pain is generally of low quality. Neither technique is appropriate when a person has an underlying medical cause for the back pain such as osteoporosis, spinal cord compression, or arthritis.
Why is back pain still a huge problem? Maybe this: “It is extremely difficult to alter the potentially disabling belief among the lay public that low back pain has a structural mechanical cause. An important reason for this is that this belief continues to be regularly reinforced by the conditions of care of a range of ‘hands-on’ providers, for whom idiosyncratic variations of that view are fundamental to their professional existence.”
The big idea of classification-based cognitive functional therapy (CB-CFT or just CFT) is that most back pain has nothing to do with scary spinal problems and so the cycle of pain and disability can be broken by easing patient fears and anxieties. For this study, CFT was tried with 62 patients and compared to 59 who were treated with manual therapy and exercise. The CFT group did better: a 13-point boost on a 100-point disability scale, and 3 points on a 10-point pain scale. As the authors put it for BodyInMind.org, “Disabling back pain can change for the better with a different narrative and coping strategies.” These results aren’t proof that the confidence cure works, but they are promising.
References to any non-Onnit entity, product, service, person or source of information in this or any other Communication should not be considered an endorsement, either direct or implied, by the host, presenter or distributor of the Communication. The host(s), presenter(s) and/or distributor(s) of this Communication are not responsible for the content of any non-Onnit internet pages referenced in the Communication. Onnit is not liable or responsible for any advice, course of treatment, diagnosis or any other information or services you chose to follow without consulting a qualified medical professional. Before starting any new diet and/or exercise program, always be sure to check with your qualified medical professional.

The hip joint is designed to withstand a fair amount of wear and tear, but it’s not indestructible. For example, when you walk, a cushion of cartilage helps prevent friction as the hip bone moves in its socket. With age and use, this cartilage can wear down or become damaged, or the hip bone itself can be fractured during a fall. In fact, more than 300,000 adults over 65 are hospitalized for hip fractures each year, according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.

If your hips are killing you, you probably spend a lot of time sitting – in the car, at work, on that spinning seat – which puts your hips in near-constant “flexion”, says Cori Lefkowith, NASM-certified personal trainer and owner of Redefining Strength in Orange County, California. Even running involves a repetitive flexion movement that can cause pain.
The condition is cauda equina syndrome. It involves “acute loss of function of the neurologic elements (nerve roots) of the spinal canal below the termination (conus) of the spinal cord,” where the nerves spread out like a horse (equina) tail. Again, this condition causes symptoms in the “saddle” of the body: butt, groin, inner thighs. BACK TO TEXT
It is sometimes hard for an aggressive athlete to consider changing training schedules. It is also hard to accept the fact that a serious disease may exist. All athletes who suffer from low back pain should seek medical advice. Some situations might require reducing or stopping athletic activity until the problem is resolved. The body's ability to be active is worth preserving.

How to: Lie on your back with your right knee bent and foot flat on the floor (a). With your left leg fully extended, press into your right foot to shift onto your left hip. This is your starting position (b). Then, squeeze your right glutes to press your left hip open until you feel a stretch, pause, then return to start. That’s one rep (c). Perform six to eight reps, then repeat on the opposite side.
Discectomy or microdiscectomy may be recommended to remove a disc, in cases where it has herniated and presses on a nerve root or the spinal cord, which may cause intense and enduring pain. Microdiscectomy is similar to a conventional discectomy; however, this procedure involves removing the herniated disc through a much smaller incision in the back and a more rapid recovery. Laminectomy and discectomy are frequently performed together and the combination is one of the more common ways to remove pressure on a nerve root from a herniated disc or bone spur.
To help you strengthen these important muscles, Miranda put together a list of exercises, below. They include dynamic warm-up moves, meant to activate your hip muscles and prep them for the bigger movements to come; functional moves that train basic movement patterns, like the squat, hip hinge, and lunge; functional plyometric exercises that train explosive power; and a few moves that get you moving in different planes of motion, or directions.
There is controversy and scientific uncertainty about trigger points. It’s undeniable that mammals suffer from sensitive spots in our soft tissues … but their nature remains unclear, and the “tiny cramp” theory could be wrong. The tiny cramp theory is formally known as the “expanded integrated hypothesis,” and it has been prominently criticized by Quintner et al (and not many others). However, it’s the mostly widely accepted explanation for now. BACK TO TEXT

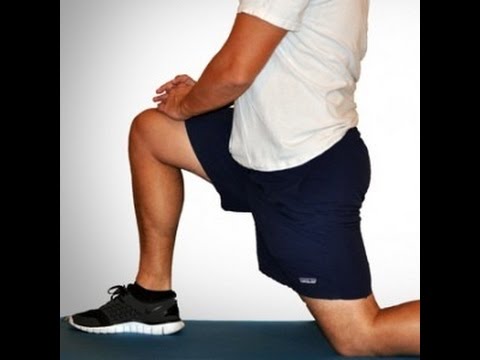
Recovering from a hip flexor injury can take time, but proper supervision and guidance from a musculoskeletal professional can minimize downtime and pain. Additionally, there are a few stretches you can do at home to recover from a hip flexor injury. The following stretch increases hip flexor dexterity, while helping alleviate pain in and around the hip and upper thigh.
Apply the above concept to your hips. When you sit, your hips are in a "flexed" position. Therefore, the muscles that flex your hips are in a shortened state. You probably spend at least a third of your day sitting down. Think about how much time those hip flexor muscles stay shortened. A lot. Over time, they become tighter and tighter until you look like the old man in the picture. So unless you want to look like that, perform the stretches shown below.
First and foremost, stop slouching. One of the most common causes of low back pain is poor sitting posture. The strain on the back while sitting in a slouched position can cause excessive pressure on the joints, muscles, and discs, causing pain. Learn to sit with correct posture and maintain that posture at all times to help decrease or eliminate your low back pain. Also be sure your workspace is set up properly at home and at work.
Without changing the position of your knees, bend at your hips and lower your torso until it’s almost parallel to the floor (or as far as you can comfortably go without rounding your back). Pause, then lift your torso back to the starting position. Be sure to squeeze your glutes and push your hips forward to lift your torso back to the starting position. This ensures you’re engaging your hip muscles instead of relying on your lower back. Do 10 reps total.
Irritable hip: What you need to know Irritable hip is a common cause of hip pain and limping in children before they reach puberty. It may happen after an injury or a viral infection, or because of poor blood flow. It usually gets better with rest within 2 weeks. Pain killers may help relieve symptoms. Those under 16 years should not use aspirin. Read now
Physician specialties that evaluate and treat low back pain range from generalists to subspecialists.These specialties include emergency medicine physicians, general medicine, family medicine, internal medicine, gynecology, spine surgeons (orthopaedics and neurosurgery), rheumatology, pain management, and physiatry. Other health care providers for low back pain include physical therapists, chiropractors, massage therapists, psychologists, and acupuncturists.
Iliopsoas syndrome, which is also called psoas syndrome or iliopsoas tendonitis, occurs when the iliopsoas muscles are injured. Lower back pain is the most common symptom; however, pain can also occur in the hip, thigh, or leg. The iliopsoas bursa, which is a fluid-filled sac located on the inside of the hip that reduces rubbing and friction, is also likely to become inflamed due to the proximity of the two structures. When this happens, the inflamed bursae will make it difficult to move.

