Congenital bone conditions: Congenital causes (existing from birth) of low back pain include scoliosis and spina bifida. Scoliosis is a sideways (lateral) curvature of the spine that can be caused when one lower extremity is shorter than the other (functional scoliosis) or because of an abnormal architecture of the spine (structural scoliosis). Children who are significantly affected by structural scoliosis may require treatment with bracing and/or surgery to the spine. Adults infrequently are treated surgically but often benefit by support bracing. Spina bifida is a birth defect in the bony vertebral arch over the spinal canal, often with absence of the spinous process. This birth defect most commonly affects the lowest lumbar vertebra and the top of the sacrum. Occasionally, there are abnormal tufts of hair on the skin of the involved area. Spina bifida can be a minor bony abnormality without symptoms. However, the condition can also be accompanied by serious nervous abnormalities of the lower extremities.
The site navigation utilizes arrow, enter, escape, and space bar key commands. Left and right arrows move across top level links and expand / close menus in sub levels. Up and Down arrows will open main level menus and toggle through sub tier links. Enter and space open menus and escape closes them as well. Tab will move on to the next part of the site rather than go through menu items.
Honestly, I am new to a lot of this stuff, so I am definitely not an expert on the subject. However, I have been doing some research on the matter, and it seems most people recommend stretching the opposing muscle group in such cases. For example, if you injured your hamstring, you would stretch your thigh. You would also want to stretch the surrounding muscle groups, seeing as how our entire body is fit together, so that every part of your body affects every other part. I realize that by now you are probably back to skating, but for anyone else who reads this and has a similar issue, I would still suggest looking into it a bit, as, like I said, I am new to a lot of stuff (PE was about as far as I got when it came to exercise, until almost two months ago, when I found crossfit), but at least it’s a start.
Doing the bridge exercise in the morning gets your muscles working, activated, and engaged and will help support you the rest of the day, says Humphrey. Lie on your back with your legs bent and your feet flat on the floor, hip-width apart. Press down through your ankles and raise your buttocks off the floor while you tighten your abdominal muscles. Keep your knees aligned with your ankles and aim for a straight line from knees to shoulders, being sure not to arch your back; hold this position for three to five seconds and then slowly lower your buttocks back to the floor. Start with one set of 10 and build up to two or three sets.

Dr. Shiel received a Bachelor of Science degree with honors from the University of Notre Dame. There he was involved in research in radiation biology and received the Huisking Scholarship. After graduating from St. Louis University School of Medicine, he completed his Internal Medicine residency and Rheumatology fellowship at the University of California, Irvine. He is board-certified in Internal Medicine and Rheumatology.
You'll need a resistance band for this one. With this exercise you're focusing on four movements—flexion, extension, abduction and adduction. Try and stand up straight while doing the exercise. If you have to lean excessively, step closer to the anchor point of your band to decrease resistance. You'll find that not only are you working the muscles of the leg that's moving, the muscles of your stance leg will work quite hard stabilizing and balancing.
^ Jump up to: a b c d e f Qaseem, A; Wilt, TJ; McLean, RM; Forciea, MA; Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of, Physicians. (4 April 2017). "Noninvasive Treatments for Acute, Subacute, and Chronic Low Back Pain: A Clinical Practice Guideline From the American College of Physicians". Annals of Internal Medicine. 166 (7): 514–530. doi:10.7326/M16-2367. PMID 28192789.
This information is not designed to replace a physician's independent judgment about the appropriateness or risks of a procedure for a given patient. Always consult your doctor about your medical conditions or back problem. SpineUniverse does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Use of the SpineUniverse.com site is conditional upon your acceptance of our User Agreement 
Nucleoplasty, also called plasma disc decompression (PDD), is a type of laser surgery that uses radiofrequency energy to treat people with low back pain associated with mildly herniated discs. Under x-ray guidance, a needle is inserted into the disc. A plasma laser device is then inserted into the needle and the tip is heated to 40-70 degrees Celsius, creating a field that vaporizes the tissue in the disc, reducing its size and relieving pressure on the nerves. Several channels may be made depending on how tissue needs to be removed to decompress the disc and nerve root.
Backpack overload in children: Low back pain unrelated to injury or other known cause is unusual in pre-teen children. However, a backpack overloaded with schoolbooks and supplies can strain the back and cause muscle fatigue. The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons recommends that a child’s backpack should weigh no more than 15 to 20 percent of the child’s body weight.
Overall, the outcome for acute low back pain is positive. Pain and disability usually improve a great deal in the first six weeks, with complete recovery reported by 40 to 90%.[2] In those who still have symptoms after six weeks, improvement is generally slower with only small gains up to one year. At one year, pain and disability levels are low to minimal in most people. Distress, previous low back pain, and job satisfaction are predictors of long-term outcome after an episode of acute pain.[2] Certain psychological problems such as depression, or unhappiness due to loss of employment may prolong the episode of low back pain.[13] Following a first episode of back pain, recurrences occur in more than half of people.[23]
The condition is cauda equina syndrome. It involves “acute loss of function of the neurologic elements (nerve roots) of the spinal canal below the termination (conus) of the spinal cord,” where the nerves spread out like a horse (equina) tail. Again, this condition causes symptoms in the “saddle” of the body: butt, groin, inner thighs. BACK TO TEXT
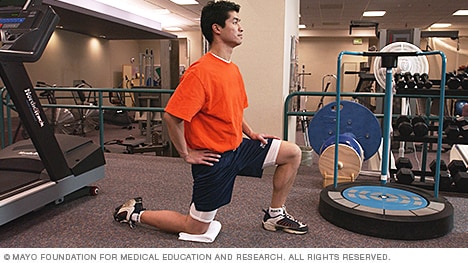
Without changing the position of your knees, bend at your hips and lower your torso until it’s almost parallel to the floor (or as far as you can comfortably go without rounding your back). Pause, then lift your torso back to the starting position. Be sure to squeeze your glutes and push your hips forward to lift your torso back to the starting position. This ensures you’re engaging your hip muscles instead of relying on your lower back. Do 10 reps total.
Neglect your lower body too often and you risk losing mobility — that thing that allows you to plop down on the floor to play with your kids, or get up and out of even the cushiest chair with ease. “A lot of people sit all day, so they’re not necessarily using their glute muscles,” says Daily Burn Fitness/Nutrition Coach Allie Whitesides. “And a lot of people are in the car all the time, so we’re not using our leg muscles much, either.”
Approximately 9–12% of people (632 million) have LBP at any given point in time, and nearly 25% report having it at some point over any one-month period.[7][8] About 40% of people have LBP at some point in their lives,[7] with estimates as high as 80% among people in the developed world.[22] Difficulty most often begins between 20 and 40 years of age.[1] Men and women are equally affected.[4] Low back pain is more common among people aged between 40 and 80 years, with the overall number of individuals affected expected to increase as the population ages.[7]
The hip is a very stable ball and socket type joint with an inherently large range of motion. The hip contains some of the largest muscle in the body as well as some of the smallest. Most people lack mobility due to a relatively sedentary lifestyle. Periods of prolonged sitting results in tightness of the hip flexors and hamstrings. Tightness in the muscles and ligaments can created joint forces that result in arthritis, postural problems, bursitis, and mechanical back pain.
Hip hikers (also known as the pelvic drop) are great exercises to get your gluteal muscles working in a weight bearing position. To do the exercise, stand sideways with one foot on a step and the other hanging off. Keeping both knees straight, lower down your pelvis on one side so your foot moves toward the floor. Both knees should remain straight; the motion should come from your hip joint. Once your pelvis is lowered down, slowly raise it back up to the starting position. Repeat the exercise for 10 repetitions.
Hip pain and stiffness is a common condition treated at Airrosti. The hip is one of the largest joints in the body. To function correctly and with full range of motion, the ligaments, muscles, and fascia surrounding the joint must be working in unison. Our providers are trained to find the source of the pain and eliminate it quickly and safely — typically in as few as three visits based on patient-reported outcomes.
The magnitude of the burden from low back pain has grown worse in recent years. In 1990, a study ranking the most burdensome conditions in the U.S. in terms of mortality or poor health as a result of disease put low back pain in sixth place; in 2010, low back pain jumped to third place, with only ischemic heart disease and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease ranking higher.
Hip flexors. These hardworking muscles are crucial in foundational movements such as sitting, standing, walking and running — they act as a bridge connecting your torso to your lower body. Some muscles in this group can be notoriously weak or tight and those of you who have ever had issues with this part of your body will know the uncomfortable pain of either all too well. There’s a lot of debate in the world of sports science over how much you should strengthen and stretch your hip flexors — we’ll explain.
Sit in a chair with good lumbar support and proper position and height for the task. Keep shoulders back. Switch sitting positions often and periodically walk around the office or gently stretch muscles to relieve tension. A pillow or rolled-up towel placed behind the small of the back can provide some lumbar support. During prolonged periods of sitting, elevate feet on a low stool or a stack of books.
MRI (or magnetic resonance imaging) scan is a radiology technique which uses magnetism, radio waves, and a computer to produce images of body structures. MRI scanning is painless and does not involve X-ray radiation. Patients with heart pacemakers, metal implants, or metal chips or clips in or around the eyes cannot be scanned with MRI because of the effect of the magnet.
“Red flags” are signs or symptoms that something medically ominous may be going on. Red flags are not reliable, and their presence is not a diagnosis. When you have some red flags, it only indicates a need to look more closely. Sometimes red flags are missing there really is something serious going on … and sometimes they are a false alarm.18 Check off all that apply … hopefully none or few or only the least alarming of them!
Spondylolisthesis. This condition occurs when one vertebra slips over the adjacent one. There are 5 types of spondylolisthesis but the most common are secondary to a defect or fracture of the pars (between the facet joints) or mechanical instability of the facet joints (degenerative). The pain can be caused by instability (back) or compression of the nerves (leg).

True numbness is not just a dead/heavy feeling (which is common, and caused even by minor muscular dysfunction in the area), but a significant or complete lack of sensitivity to touch. You have true numbness when you have patches of skin where you cannot feel light touch. Such areas might still be sensitive to pressure: you could feel a poke, but as if it was through a layer of rubber. Most people have experienced true numbness at the dentist. BACK TO TEXT
Along with these exercises, it's also important to do some supplementary exercises to work your hip's supporting muscles. You've probably heard of your shoulder's rotator cuff. Well, your hip also has a cuff, or a group of muscles that help stabilize and support movement. For these exercises, you'll need a mini-band, a longer thera-band or tubing (both are sold at many sporting goods stores, or can be purchased online), and a cable-column unit.
Im a skateboarder and a couple weeks ago i skated alot every day and my lefy hip was starting to get sore. But of course i couldnt resist skating so i kept skating and it got worse and worse to the point i couldnt really skate at all without my hip hurting but of course i would still mess around on the board doing tiny tricks but a couple days ago i was just skating around not really doing tricks and i slipped and kicked my leg out and REALLY hurt my hip and thought i tore a tendon or something and couldnt walk for two days, but its gotten alot better and i can walk fairly normal and i ice it everyday but whenever i stretch it its just a really sharp pain it doesnt feel like im stretching it. What do i do when all the stretch does is make a sharp pain? How do i strengthen my hip? And how long would it take to strengthen my hip to full strength again? Because i cant stand not being able to skate. Please reply so i can skate as soon as possible thank you
Those are some great stretches! I own a personal training studio in Severna Park, Maryland. Majority of my clients have physical limitations – so it’s important for them to stay flexible. I send these to my clients and even do these exercises for myself. I highly recommend these stretches to anyone, even people without physical limitations. I love the fact these are actually videos and not just stretches because it’s so much easier for people to figure out how to perform the stretches. You guys are the real MVP!

Athletes are at greater risk of sustaining a lumber spine injury due to physical activity. Whether the sport is skiing, basketball, football, gymnastics, soccer, running, golf, or tennis-the spine undergoes a lot of stress, absorption of pressure, twisting, turning, and even bodily impact. This strenuous activity puts stress on the back that can cause injury to even the finest and most fit athletes.

The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2019, A.D.A.M., Inc. Duplication for commercial use must be authorized in writing by ADAM Health Solutions.
Talmage, J; Belcourt, R; Galper, J; et al. (2011). "Low back disorders". In Kurt T. Hegmann. Occupational medicine practice guidelines : evaluation and management of common health problems and functional recovery in workers (3rd ed.). Elk Grove Village, IL: American College of Occupational and Environmental Medicine. pp. 336, 373, 376–377. ISBN 978-0615452272.
The hip joint is where the ball of the thigh bone (femur) joins the pelvis at a socket called the acetabulum. There is cartilage covering both the bone of the femur and the acetabulum of the pelvis in the hip joint. A joint lining tissue, called synovium, surrounds the hip joint. The synovium tissue produces fluid that lubricates the joint and provides nutrients to the cartilage of the joint. The ligaments around the hip joint attach the femur bone to the bony pelvis. There are a number of muscles and tendons that glide around the hip joint. Tiny fluid-filled sacs, called bursae, provide gliding surfaces for muscles and tendons around the hip joint. Major arteries and veins pass the front of the hip joint. The largest nerve of the body, the sciatic nerve, passes behind the hip joint.
Meanwhile, many non-dangerous problems can cause amazingly severe back pain. A muscle cramp is a good analogy — just think about how painful a Charley horse is! Regardless of what’s actually going on in there, muscle pain is probably the main thing that back pain patients are feeling. The phenomenon of trigger points — tiny muscle cramps, basically11 — could be the entire problem, or a complication that’s more painful and persistent than the original problem. It’s hard to overstate how painful trigger points can be, but they are not dangerous to anything but your comfort.
When I do a deep knee bend like a sumo squat I get a popping in the outside of my left knee. It feels like a big tendon or ligament is slipping per something. It isn’t painful peer se but I’m afraid if I do it a lot it will be. Is that a relatively common symptom for a guy with tight flexors, it bands, etc? Should I just push through it or have it checked out?


