Kneel on your mat with thighs perpendicular to the floor and tops of of your feet facing down. Place a yoga block between your feet. Bring your inner knees together. Slide your feet apart so they are slightly wider than your hips, and press the tops of your feet evenly into the mat. Slowly sit down on the yoga block. Use your hands to turn the top of your thighs inward. Allow the backs of your hands to rest on your thighs. Hold for at least 30 seconds.
An intervertebral disc has a gelatinous core surrounded by a fibrous ring.[32] When in its normal, uninjured state, most of the disc is not served by either the circulatory or nervous systems – blood and nerves only run to the outside of the disc.[32] Specialized cells that can survive without direct blood supply are in the inside of the disc.[32] Over time, the discs lose flexibility and the ability to absorb physical forces.[25] This decreased ability to handle physical forces increases stresses on other parts of the spine, causing the ligaments of the spine to thicken and bony growths to develop on the vertebrae.[25] As a result, there is less space through which the spinal cord and nerve roots may pass.[25] When a disc degenerates as a result of injury or disease, the makeup of a disc changes: blood vessels and nerves may grow into its interior and/or herniated disc material can push directly on a nerve root.[32] Any of these changes may result in back pain.[32]
Sit in a chair with good lumbar support and proper position and height for the task. Keep shoulders back. Switch sitting positions often and periodically walk around the office or gently stretch muscles to relieve tension. A pillow or rolled-up towel placed behind the small of the back can provide some lumbar support. During prolonged periods of sitting, elevate feet on a low stool or a stack of books.
Congenital bone conditions: Congenital causes (existing from birth) of low back pain include scoliosis and spina bifida. Scoliosis is a sideways (lateral) curvature of the spine that can be caused when one lower extremity is shorter than the other (functional scoliosis) or because of an abnormal architecture of the spine (structural scoliosis). Children who are significantly affected by structural scoliosis may require treatment with bracing and/or surgery to the spine. Adults infrequently are treated surgically but often benefit by support bracing. Spina bifida is a birth defect in the bony vertebral arch over the spinal canal, often with absence of the spinous process. This birth defect most commonly affects the lowest lumbar vertebra and the top of the sacrum. Occasionally, there are abnormal tufts of hair on the skin of the involved area. Spina bifida can be a minor bony abnormality without symptoms. However, the condition can also be accompanied by serious nervous abnormalities of the lower extremities.
Just because your hip flexor region feels sore doesn’t necessarily mean the muscles there are tight — in fact, they might need strengthening. This is where that sports science debate we mentioned earlier comes into play. It’s important to identify whether you’re tight or if the muscles are weak. Again, the Thomas Test will help you identify if you’re maybe stretching something that actually needs strengthening.

As has been highlighted by research presented at the national meeting of the American College of Rheumatology, a very important aspect of the individual evaluation is the patient's own understanding and perception of their particular situation. British researchers found that those who believed that their symptoms had serious consequences on their lives and that they had, or treatments had, little control over their symptoms were more likely to have a poor outcome. This research points out to physicians the importance of addressing the concerns and perceptions that patients have about their condition during the initial evaluations.
Really great content. I also had some lower back problem but now that I know the source, I will work on it. My counsins also talked to me about this product called Panifix, or "Unlock your hip flexor" which Gives You A Practical, Easy-to-follow Program You Can Use To Instantly Release Your Hip Flexors For More Strength, Better Health And All Day Energy. Proven Swipes And Creatives Here:https://tinyurl.com/yd6nbzfh
How to: Lie on your back with your right knee bent and foot flat on the floor (a). With your left leg fully extended, press into your right foot to shift onto your left hip. This is your starting position (b). Then, squeeze your right glutes to press your left hip open until you feel a stretch, pause, then return to start. That’s one rep (c). Perform six to eight reps, then repeat on the opposite side. 
Simply stand up straight with your feet about shoulder-width apart. Slowly bend your knees and hips, lowering yourself until your knees obscure your toes or you achieve a 90 degree angle. Hold for a count of 5 and then gently resume your original position. This can be a tough one so again, don’t overdo it and hold on to a table if you need a little extra support! Try to repeat between 5-10 times.
In this study, one patient with sciatica was sent for ten MRIs, which produced 49 distinct “findings,” 16 of them unique, none of which occurred in all ten reports. On average, each radiologist made about a dozen errors, seeing one or two things that weren’t there and missing about ten things that were. Yikes. Read a more detailed and informal description of this study.
Luckily, you don’t have to quit your day job or forgo spin class to loosen them up. Simply stretching those hips can get your body back in alignment, increase your mobility (and thus your exercise performance) and maybe even ease pesky back pain, Moore says. “Given the amount of time we sit [each] day and the stress we put our bodies under, hip-opening moves are a necessary party of our daily routine.”

Contact sports: It should go without saying; all contact sports should be firmly off your to-do list! That also includes sports than involve contact with another object like tennis or gold! Not only do these forms of exercise make you vulnerable to further injury, the rigorous movements required can place your hip joint under too much stress. Try and give the footie a miss for now and instead focus on other exercises you can do with your friends such as swimming or yoga!
It is not clear whether men or women have higher rates of low back pain.[7][8] A 2012 review reported a rate of 9.6% among males and 8.7% among females.[8] Another 2012 review found a higher rate in females than males, which the reviewers felt was possibly due to greater rates of pains due to osteoporosis, menstruation, and pregnancy among women, or possibly because women were more willing to report pain than men.[7] An estimated 70% of women experience back pain during pregnancy with the rate being higher the further along in pregnancy.[97] Current smokers – and especially those who are adolescents – are more likely to have low back pain than former smokers, and former smokers are more likely to have low back pain than those who have never smoked.[98]
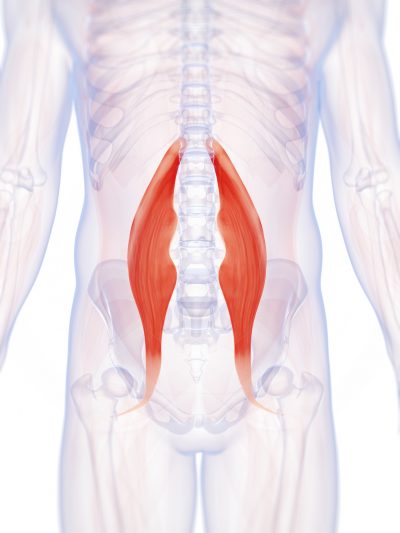
A sedentary lifestyle can lead to having weak and tight hip flexors as they are always in the shortened position. Tight hip flexors can lead to a limited range of motion, poor posture, lower back, and hip pain, and even injuries. These muscles need to get a workout when you are standing and doing movements such as raising your leg to climb stairs, run, or ride a bicycle.
When I do a deep knee bend like a sumo squat I get a popping in the outside of my left knee. It feels like a big tendon or ligament is slipping per something. It isn’t painful peer se but I’m afraid if I do it a lot it will be. Is that a relatively common symptom for a guy with tight flexors, it bands, etc? Should I just push through it or have it checked out?
It is sometimes hard for an aggressive athlete to consider changing training schedules. It is also hard to accept the fact that a serious disease may exist. All athletes who suffer from low back pain should seek medical advice. Some situations might require reducing or stopping athletic activity until the problem is resolved. The body's ability to be active is worth preserving.

Start in a runner’s lunge, right leg forward with knee over ankle and left knee on ground with top of your foot flat on the mat. Slowly lift torso and rest hands lightly on right thigh. Lean hips forward slightly, keeping right knee behind toes, and feel the stretch in the left hip flexor. Hold here, or for a deeper stretch, raise arms overhead, biceps by ears. Hold for at least 30 seconds, then repeat on opposite side.
A complete medical history and physical exam can usually identify any serious conditions that may be causing the pain. During the exam, a health care provider will ask about the onset, site, and severity of the pain; duration of symptoms and any limitations in movement; and history of previous episodes or any health conditions that might be related to the pain. Along with a thorough back examination, neurologic tests are conducted to determine the cause of pain and appropriate treatment. The cause of chronic lower back pain is often difficult to determine even after a thorough examination.
According to a study published in Annals of Internal Medicine, there is strong evidence that yoga can have a short-term effect on treating lower back pain. Yoga involves slow, controlled movements to stretch and strengthen the body. This exercise form also promotes stress relief, which can help reduce tension you may commonly hold in your lower back.
It is sometimes hard for an aggressive athlete to consider changing training schedules. It is also hard to accept the fact that a serious disease may exist. All athletes who suffer from low back pain should seek medical advice. Some situations might require reducing or stopping athletic activity until the problem is resolved. The body's ability to be active is worth preserving.
According to a study published in Annals of Internal Medicine, there is strong evidence that yoga can have a short-term effect on treating lower back pain. Yoga involves slow, controlled movements to stretch and strengthen the body. This exercise form also promotes stress relief, which can help reduce tension you may commonly hold in your lower back.
Degenerative Conditions: Sometimes, degenerative conditions that are the normal result of aging may cause your low back pain. Conditions like spinal stenosis, arthritis, or degenerative disc disease can all cause pain. Congenital conditions, like spondylolisthesis or scoliosis, can also cause your back pain. For most degenerative back problems, movement and exercise have been proven to be effective in treating these conditions. A visit to your physical therapist can help you determine the correct progression of back exercises for your specific condition.
Really a great content. Let me tell you first about hip flexor it is the engine through which our body moves. They control balance, our ability to sit, stand, twist, reach, bend, walk and step. One of my patient also suffering from same problem but due to lack of money he was unable to afford a treatment. So i recommend him a program to unlock hip flexor. If anyone wants they can check it out here ;- https://tinyurl.com/y8yaqs2s Report
Model Zach Job is a New-York based artist and producer who is also an up-and-coming drag queen known as "Glow Job." Zach has aspirations to join a circus and thus has some training in gymnastics, silks/wall running, parkour, boxing, dance, and acro-yoga. He also swings kettlebells at New York's Mark Fisher Fitness, climbs rocks at Brooklyn Boulders, bicycles 10-20 miles every day, and plays competitive dodgeball.
Long periods of inactivity in bed are no longer recommended, as this treatment may actually slow recovery. Spinal manipulation for periods of up to one month has been found to be helpful in some patients who do not have signs of nerve irritation. Future injury is avoided by using back-protection techniques during activities and support devices as needed at home or work.

The big idea of classification-based cognitive functional therapy (CB-CFT or just CFT) is that most back pain has nothing to do with scary spinal problems and so the cycle of pain and disability can be broken by easing patient fears and anxieties. For this study, CFT was tried with 62 patients and compared to 59 who were treated with manual therapy and exercise. The CFT group did better: a 13-point boost on a 100-point disability scale, and 3 points on a 10-point pain scale. As the authors put it for BodyInMind.org, “Disabling back pain can change for the better with a different narrative and coping strategies.” These results aren’t proof that the confidence cure works, but they are promising.


