So, who cares right? Wrong. Everyone has seen that little old man walking with a cane, hunched over almost to the point of staring at the ground. Do you think he always walked like that? I'd bet you he didn't. Maybe he had an injury that never healed properly, or maybe after spending years and years in a similar position, his body became tighter and tighter until eventually he ended up bent over.
Avoiding injury to the low back is a method of preventing low back pain. Additionally, conditioning exercise programs designed to strengthen the lumbar area and adjacent tissues can help to minimize risk of injury to the low back. Specific programs to relieve and prevent back pain can be designed with the help of physical therapists and other treating health-care professionals.
Hip tendonitis is inflammation of any of the hip tendons, or thick cords that attach muscles to bone. Similar to strains, hip tendonitis is commonly caused by overuse. And, also like strains, tendonitis frequently affects the same population—athletes who participate in cycling, swimming, running, and other sports that repeatedly stress the hip. High intensity interval training (HIIT) workouts and other activities that involve a high volume of kicking, squatting, and jumping can also lead to tendon inflammation.
It is unclear if among those with non-chronic back pain alternative treatments are useful.[84] For chiropractic care or spinal manipulation therapy (SMT) it is unclear if it improves outcomes more or less than other treatments.[18] Some reviews find that SMT results in equal or better improvements in pain and function when compared with other commonly used interventions for short, intermediate, and long-term follow-up;[19][20][85] other reviews find it to be no more effective in reducing pain than either inert interventions, sham manipulation, or other treatments, and conclude that adding SMT to other treatments does improve outcomes.[17][21] National guidelines reach different conclusions, with some not recommending spinal manipulation, some describing manipulation as optional, and others recommending a short course for those who do not improve with other treatments.[3] A 2017 review recommended spinal manipulation based on low quality evidence.[6] Manipulation under anaesthesia, or medically assisted manipulation, has not enough evidence to make any confident recommendation.[86]
Workers who experience acute low back pain as a result of a work injury may be asked by their employers to have x-rays.[102] As in other cases, testing is not indicated unless red flags are present.[102] An employer's concern about legal liability is not a medical indication and should not be used to justify medical testing when it is not indicated.[102] There should be no legal reason for encouraging people to have tests which a health care provider determines are not indicated.[102]
The hip is a common site of osteoarthritis. To help protect the hip joint from "wear and tear," it is important to strengthen the muscles that support it. Your hip also controls the position of your knee, and strengthening your hips may be one component of your rehab program for knee pain. Your physical therapist may also prescribe hip exercises after total hip replacement if you have a hip labrum tear or as part of your hip exercise program for hip pain.

Low back pain results in large economic costs. In the United States, it is the most common type of pain in adults, responsible for a large number of missed work days, and is the most common musculoskeletal complaint seen in the emergency department.[25] In 1998, it was estimated to be responsible for $90 billion in annual health care costs, with 5% of individuals incurring most (75%) of the costs.[25] Between 1990 and 2001 there was a more than twofold increase in spinal fusion surgeries in the US, despite the fact that there were no changes to the indications for surgery or new evidence of greater usefulness.[11] Further costs occur in the form of lost income and productivity, with low back pain responsible for 40% of all missed work days in the United States.[101] Low back pain causes disability in a larger percentage of the workforce in Canada, Great Britain, the Netherlands and Sweden than in the US or Germany.[101]
In this study, one patient with sciatica was sent for ten MRIs, which produced 49 distinct “findings,” 16 of them unique, none of which occurred in all ten reports. On average, each radiologist made about a dozen errors, seeing one or two things that weren’t there and missing about ten things that were. Yikes. Read a more detailed and informal description of this study.
The hip is a basic ball-and-socket joint. The ball is the femoral head—a knob on the top of the thigh bone—and the socket is an indentation in the pelvic bone. There is cartilage lining the joint (called the labrum) and ligaments that attach the pelvic and thigh bones. Numerous muscles attach around the hip, too, moving the joint through the basic motions of flexion (bending), extension (extending the leg behind you), abduction (lifting the leg away from the body), adduction (moving the leg inward), internal rotation, and external rotation.

How to: Sit down with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor in front of you (a). Place your right ankle on top of your left thigh and flex your right foot (b). Put your hands behind your body, fingertips facing away from your body and begin to press your hips toward your heels until you feel a stretch through your outer left hip. Keep your back tall and chest open (c). Hold for six to eight breaths, then repeat on the other side.
At the start of the 20th century, physicians thought low back pain was caused by inflammation of or damage to the nerves,[99] with neuralgia and neuritis frequently mentioned by them in the medical literature of the time.[100] The popularity of such proposed causes decreased during the 20th century.[100] In the early 20th century, American neurosurgeon Harvey Williams Cushing increased the acceptance of surgical treatments for low back pain.[14] In the 1920s and 1930s, new theories of the cause arose, with physicians proposing a combination of nervous system and psychological disorders such as nerve weakness (neurasthenia) and female hysteria.[99] Muscular rheumatism (now called fibromyalgia) was also cited with increasing frequency.[100]
The story of actor Andy Whitfield is a disturbing and educational example of a case that met these conditions — for sure the first two, and probably the third as well if we knew the details. Whitfield was the star of the hit TV show Spartacus (which is worthwhile, but rated very, very R17). The first sign of the cancer that killed him in 2011 was steadily worsening back pain. It’s always hard to diagnose a cancer that starts this way, but Whitfield was in the middle of intense physical training to look the part of history’s most famous gladiator. Back pain didn’t seem unusual at first, and some other symptoms may have been obscured. Weight loss could have even seemed like a training victory at first! It was many long months before he was diagnosed — not until the back pain was severe and constant. A scan finally revealed a large tumour pressing against his spine.
Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty are minimally invasive treatments to repair compression fractures of the vertebrae caused by osteoporosis. Vertebroplasty uses three-dimensional imaging to assist in guiding a fine needle through the skin into the vertebral body, the largest part of the vertebrae. A glue-like bone cement is then injected into the vertebral body space, which quickly hardens to stabilize and strengthen the bone and provide pain relief. In kyphoplasty, prior to injecting the bone cement, a special balloon is inserted and gently inflated to restore height to the vertebral structure and reduce spinal deformity.
Your hip labrum is a band of cartilage-like tissue that courses around the outer rim of your hip socket. This labrum helps to support the joint and deepen the socket. Sometimes overuse or an injury to your hip can cause a tear in your labrum. A hip labrum tear may result in a condition called femoroacetabular impingement (FAI). When this happens, hip pain may result, and exercises to stretch and stabilize your hip may be performed.

If you are experiencing low back pain, you are not alone. An estimated 75 to 85 percent of all Americans will experience some form of back pain during their lifetime. Although low back pain can be quite debilitating and painful, in about 90 percent of all cases, pain improves without surgery. However, 50 percent of all patients who suffer from an episode of low back pain will have a recurrent episode within one year.
Paget's disease of the bone is a condition of unknown cause in which the bone formation is out of synchrony with normal bone remodeling. This condition results in abnormally weakened bone and deformity and can cause localized bone pain, though it often causes no symptoms. Paget's disease is more common in people over the age of 50. Heredity (genetic background) and certain unusual virus infections have been suggested as causes. Thickening of involved bony areas of the lumbar spine can cause the radiating lower extremity pain of sciatica.
This Web site provides general educational information on health-related issues and provides access to health-related resources for the convenience of our users. This site and its health-related information and resources are not a substitute for professional medical advice or for the care that patients receive from their physicians or other health care providers.
Initial management with non–medication based treatments is recommended.[6] NSAIDs are recommended if these are not sufficiently effective.[6] Normal activity should be continued as much as the pain allows.[2] Medications are recommended for the duration that they are helpful.[13] A number of other options are available for those who do not improve with usual treatment. Opioids may be useful if simple pain medications are not enough, but they are not generally recommended due to side effects.[4][13] Surgery may be beneficial for those with disc-related chronic pain and disability or spinal stenosis.[14][15] No clear benefit has been found for other cases of non-specific low back pain.[14] Low back pain often affects mood, which may be improved by counseling or antidepressants.[13][16] Additionally, there are many alternative medicine therapies, including the Alexander technique and herbal remedies, but there is not enough evidence to recommend them confidently.[17] The evidence for chiropractic care[18] and spinal manipulation is mixed.[17][19][20][21]

The iliopsoas muscles are a group of two muscles—the psoas muscle and the iliacus muscle—located toward the front of the inner hip. The psoas muscles, in particular, is located in the lumbar (lower) region of the spine and extends through the pelvis to the femur. The iliopsoas muscles are the primary hip flexors, pulling the knee up off the ground when it contracts. Because the psoas muscle is also connected to the spine, it contributes to upright posture, assists in lumbar spine movement, and influences the spine’s curve.
Swimming is a low impact form of exercise that can help to relieve the pressure on your joints. It’s thought that water aerobics may help to reduce the impact on your joints by up to 75%!2 Be careful though; start with a beginner’s class and always do only what you’re comfortable with – try to avoid over-exercising or pushing your muscles too far!
The AANS does not endorse any treatments, procedures, products or physicians referenced in these patient fact sheets. This information is provided as an educational service and is not intended to serve as medical advice. Anyone seeking specific neurosurgical advice or assistance should consult his or her neurosurgeon, or locate one in your area through the AANS’ Find a Board-certified Neurosurgeon” online tool.
Recovering from a hip flexor injury can take time, but proper supervision and guidance from a musculoskeletal professional can minimize downtime and pain. Additionally, there are a few stretches you can do at home to recover from a hip flexor injury. The following stretch increases hip flexor dexterity, while helping alleviate pain in and around the hip and upper thigh.
Hi John, Thank you for the video and instructions. My question to you is that I’m schedule to have a reconstructive hip repair (Laberal tear) in July for my right hip and (second) and told that I have a tear in the right as well. I’ve been suffering from back pain too and know its because of the hips and my sitting because of work. If I can tolerate the exercise, would your recommend to do them? And if so, should I take it down from your suggested reps? I’ve been doing DDP Yoga for the last week and besides general soreness and some discomfort in my right hip, i’ve been able to make it through a full workout as well as do the core exercises. Your response would be greatly appreciated.
If you are experiencing low back pain, you are not alone. An estimated 75 to 85 percent of all Americans will experience some form of back pain during their lifetime. Although low back pain can be quite debilitating and painful, in about 90 percent of all cases, pain improves without surgery. However, 50 percent of all patients who suffer from an episode of low back pain will have a recurrent episode within one year.
Contact sports: It should go without saying; all contact sports should be firmly off your to-do list! That also includes sports than involve contact with another object like tennis or gold! Not only do these forms of exercise make you vulnerable to further injury, the rigorous movements required can place your hip joint under too much stress. Try and give the footie a miss for now and instead focus on other exercises you can do with your friends such as swimming or yoga!
Disk tear. Small tears to the outer part of the disk (annulus) sometimes occur with aging. Some people with disk tears have no pain at all. Others can have pain that lasts for weeks, months, or even longer. A small number of people may develop constant pain that lasts for years and is quite disabling. Why some people have pain and others do not is not well understood.
The Reclined Hip Stretch is a Pilates mat exercise that is one of the best stretching exercises for the outside of the hip. It looks like a pretzel move, but once you get it figured out, it feels great. It is easy and you can control how intense the stretch is. It is a good warm-up stretch, and you might use it as one of the stretches you do each morning, especially if you have tight hips.
Here is how you do the hip rotation stretch: Sit on the floor with your knee out straight. Cross one leg over the other by placing your ankle on top of your knee (as if crossing your legs while sitting). Gently pull your knee across your body, and hold for five seconds. Then gently push the knee of the top leg away from you until a stretch is felt in your hip. Hold this position for five seconds, then slowly release. Repeat 10 times.
Kneel on your mat with thighs perpendicular to the floor and tops of of your feet facing down. Place a yoga block between your feet. Bring your inner knees together. Slide your feet apart so they are slightly wider than your hips, and press the tops of your feet evenly into the mat. Slowly sit down on the yoga block. Use your hands to turn the top of your thighs inward. Allow the backs of your hands to rest on your thighs. Hold for at least 30 seconds.
Of course, you know what it feels like to have a tight muscle. But tight hips aren't just uncomfortable—they can lead to all sorts of other aches and pains, especially in the lower back. "People focus on the hips and say their hips are tight, but we don't always think about the fact that the lower back connects to our legs at the hip," Charlee Atkins, C.S.C.S., instructor at Soul Annex in New York City and creator of Le Stretch class, tells SELF. Tight hip flexors make it harder for your pelvis to rotate properly, which can cause your lower back to overcompensate, "and this can be a setup for lower-back injury," Teo Mendez, M.D., an orthopedic surgeon at NY Orthopedics who focuses on operative and non-operative management of sports-related injuries, musculoskeletal injuries, and arthritis, tells SELF.
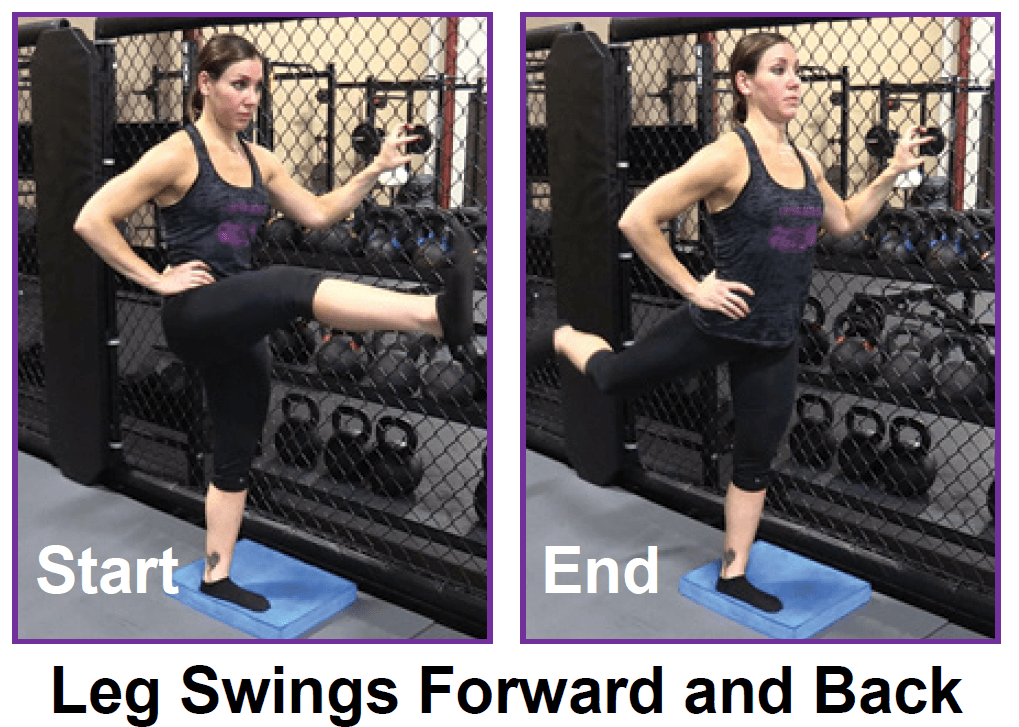
You'll need a resistance band for this one. With this exercise you're focusing on four movements—flexion, extension, abduction and adduction. Try and stand up straight while doing the exercise. If you have to lean excessively, step closer to the anchor point of your band to decrease resistance. You'll find that not only are you working the muscles of the leg that's moving, the muscles of your stance leg will work quite hard stabilizing and balancing.
For persistent low back pain, the short-term outcome is also positive, with improvement in the first six weeks but very little improvement after that. At one year, those with chronic low back pain usually continue to have moderate pain and disability.[2] People at higher risk of long-term disability include those with poor coping skills or with fear of activity (2.5 times more likely to have poor outcomes at one year),[96] those with a poor ability to cope with pain, functional impairments, poor general health, or a significant psychiatric or psychological component to the pain (Waddell's signs).[96]
Lie on your back with your knees bent and your feet flat on the floor. Tighten the muscles in your buttocks, then lift your hips off the ground and hold for about five seconds before slowly lowering yourself back down. Be sure to breathe throughout the exercise. As with the first exercise, you can work up to doing 30 repetitions, resting for a few seconds (or longer) between each. “If you start to get tired, stop and rest for a couple of minutes,” Pariser says.


