
If back pain doesn't go away in three months, there's evidence that yoga can help. In one study, people who took 12 weeks of yoga classes had fewer symptoms of low back pain than people who were given a book about care for back pain. The benefits lasted several months after the classes were finished. The study suggests conventional stretching also works just as well. Make sure your instructor is experienced at teaching people with back pain and will modify postures for you as needed.
Hip tendonitis is inflammation of any of the hip tendons, or thick cords that attach muscles to bone. Similar to strains, hip tendonitis is commonly caused by overuse. And, also like strains, tendonitis frequently affects the same population—athletes who participate in cycling, swimming, running, and other sports that repeatedly stress the hip. High intensity interval training (HIIT) workouts and other activities that involve a high volume of kicking, squatting, and jumping can also lead to tendon inflammation.
When I do a deep knee bend like a sumo squat I get a popping in the outside of my left knee. It feels like a big tendon or ligament is slipping per something. It isn’t painful peer se but I’m afraid if I do it a lot it will be. Is that a relatively common symptom for a guy with tight flexors, it bands, etc? Should I just push through it or have it checked out?

The condition is cauda equina syndrome. It involves “acute loss of function of the neurologic elements (nerve roots) of the spinal canal below the termination (conus) of the spinal cord,” where the nerves spread out like a horse (equina) tail. Again, this condition causes symptoms in the “saddle” of the body: butt, groin, inner thighs. BACK TO TEXT
Cancel, pause, or adjust your order at any time, hassle free. Your credit card will only be charged when your order ships. The discount applied every time is 15% off. Since it would be weird to subscribe to a kettlebell, the subscriptions and subscription discounts are only for things you'll need often, like supplements, foods, and personal care items. 
Paget's disease can be diagnosed on plain X-rays. However, a bone biopsy is occasionally necessary to ensure the accuracy of the diagnosis. Bone scanning is helpful to determine the extent of the disease, which can involve more than one bone area. A blood test, alkaline phosphatase, is useful for diagnosis andmonitoring response to therapy. Treatment options include aspirin, other anti-inflammatory medicines, pain medications, and medications that slow therate of bone turnover, such as calcitonin (Calcimar, Miacalcin), etidronate (Didronel), alendronate (Fosamax), risedronate (Actonel), and pamidronate (Aredia).
Low back pain (LBP) is a common disorder involving the muscles, nerves, and bones of the back.[4] Pain can vary from a dull constant ache to a sudden sharp feeling.[4] Low back pain may be classified by duration as acute (pain lasting less than 6 weeks), sub-chronic (6 to 12 weeks), or chronic (more than 12 weeks).[3] The condition may be further classified by the underlying cause as either mechanical, non-mechanical, or referred pain.[5] The symptoms of low back pain usually improve within a few weeks from the time they start, with 40–90% of people completely better by six weeks.[2]
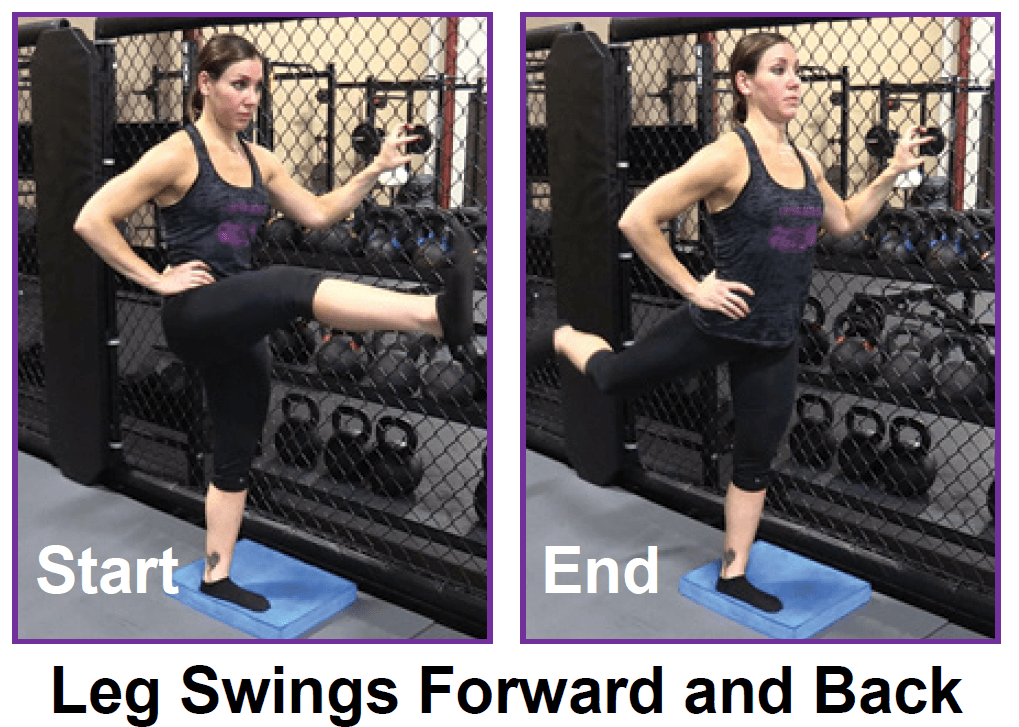
Stand tall with your hips square and bend your right knee, bringing your foot towards your bum. Grab the right foot with your right hand and actively pull the foot closer to your glutes. As you do this, send the right knee down towards the ground and keep both knees together. squeeze your butt to promote a posterior pelvic tilt and hold — then switch sides.
Walking is an easy way to strengthen your bones and muscles, burn calories, and lift your mood. If you don't currently walk for exercise, try walking for five to 10 minutes every day. Gradually build up to 30 minutes a day. It's easy to sneak walking into your day. Take up golf, window-shop at a large mall, or visit a walking-only destination, such as a museum or botanical garden.
If back pain doesn't go away in three months, there's evidence that yoga can help. In one study, people who took 12 weeks of yoga classes had fewer symptoms of low back pain than people who were given a book about care for back pain. The benefits lasted several months after the classes were finished. The study suggests conventional stretching also works just as well. Make sure your instructor is experienced at teaching people with back pain and will modify postures for you as needed.
Lumbar radiculopathy: Lumbar radiculopathy is nerve irritation that is caused by damage to the discs between the vertebrae. Damage to the disc occurs because of degeneration ("wear and tear") of the outer ring of the disc, traumatic injury, or both. As a result, the central softer portion of the disc can rupture (herniate) through the outer ring of the disc and abut the spinal cord or its nerves as they exit the bony spinal column. This rupture is what causes the commonly recognized "sciatica" pain of a herniated disc that shoots from the low back and buttock down the leg. Sciatica can be preceded by a history of localized low-back aching or it can follow a "popping" sensation and be accompanied by numbness and tingling. The pain commonly increases with movements at the waist and can increase with coughing or sneezing. In more severe instances, sciatica can be accompanied by incontinence of the bladder and/or bowels. The sciatica of lumbar radiculopathy typically affects only one side of the body, such as the left side or right side, and not both. Lumbar radiculopathy is suspected based on the above symptoms. Increased radiating pain when the lower extremity is lifted supports the diagnosis. Nerve testing (EMG/electromyogramspina bifida
Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty are minimally invasive treatments to repair compression fractures of the vertebrae caused by osteoporosis. Vertebroplasty uses three-dimensional imaging to assist in guiding a fine needle through the skin into the vertebral body, the largest part of the vertebrae. A glue-like bone cement is then injected into the vertebral body space, which quickly hardens to stabilize and strengthen the bone and provide pain relief. In kyphoplasty, prior to injecting the bone cement, a special balloon is inserted and gently inflated to restore height to the vertebral structure and reduce spinal deformity.
This standard recommendation reinforces the alarming idea that low back pain that lasts longer than a few weeks is Really Bad News. It’s not. It’s a clue. It’s a reason for concern and alertness. But many cases of low back pain that last for 6 weeks will still go away. Once again, see the 2009 research published in the British Medical Journal, which showed that more than 30% of patients with “new” chronic low back pain will still recover without treatment. BACK TO TEXT
Hip labral tear. This is a rip in the ring of cartilage (called the labrum) that follows the outside rim of the socket of your hip joint. Along with cushioning your hip joint, your labrum acts like a rubber seal or gasket to help hold the ball at the top of your thighbone securely within your hip socket. Athletes and people who perform repetitive twisting movements are at higher risk of developing this problem.
There are many causes of hip joint pain. Some hip pain is temporary, while other hip pain can be long-standing or chronic. Causes of hip pain include arthritis, inflammatory and noninflammatory arthritis, fracture, sprain, infectious arthritis (septic arthritis), avascular necrosis, Gaucher's disease, sciatica, muscle strain, iliotibial band syndrome (IT band syndrome), and hematoma.
Low back pain is not a specific disease but rather a complaint that may be caused by a large number of underlying problems of varying levels of seriousness.[25] The majority of LBP does not have a clear cause[1] but is believed to be the result of non-serious muscle or skeletal issues such as sprains or strains.[26] Obesity, smoking, weight gain during pregnancy, stress, poor physical condition, poor posture and poor sleeping position may also contribute to low back pain.[26] A full list of possible causes includes many less common conditions.[5] Physical causes may include osteoarthritis, degeneration of the discs between the vertebrae or a spinal disc herniation, broken vertebra(e) (such as from osteoporosis) or, rarely, an infection or tumor of the spine.[27]
Located deep in the front of the hip and connecting the leg, pelvis, and abdomen, the hip flexors— surprise, surprise— flex the hip. But despite being some of the most powerful muscles in our bodies (with a clearly important role), it’s easy to neglect our poor hip flexors— often without even knowing it. It turns out just working at a desk all day (guilty!) can really weaken hip flexors since they tend to shorten up while in a seated position. This tightness disrupts good posture and is a common cause of lower back pain. Weakened hip flexors can also increase the risk of foot, ankle, and knee injuries (especially among runners) Hip muscle weakness and overuse injuries in recreational runners. Niemuth, P.E., Johnson, R.J., Myers, M.J., et al. Rocky Mountain University of Health Professions, Provo, VT. Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine, 2005 Jan; 15 (1): 14-21.. So be sure to get up, stand up every hour or so! And giving the hip flexors some extra attention is not just about injury prevention. Adding power to workouts, working toward greater flexibility, and getting speedier while running is also, as they say, all in the hips The effect of walking speed on muscle function and mechanical energetics. Neptune, R.R., Sasaki, K., and Kautz, S.A. Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Texas, Austin, TX. Gait & Posture, 2008 Jul; 28 (1): 135-43..
Beacon Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine, Ltd. complies with applicable Federal civil rights laws and does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, age, disability, or sex. If you speak a language other than English, language assistance services, free of charge, are available to you. Call the Call Center at (513) 354-3700. Español (Spanish): ATENCIÓN: Si habla español, tiene a su disposición servicios gratuitos de asistencia lingüística. Llame al Call Center at (513) 354-3700. 繁體中文 (Chinese): 注意:如果您使用繁體中文,您可以免費獲得語言援助服務。請致電 Call Center at (513) 354-3700.
Paget's disease of the bone is a condition of unknown cause in which the bone formation is out of synchrony with normal bone remodeling. This condition results in abnormally weakened bone and deformity and can cause localized bone pain, though it often causes no symptoms. Paget's disease is more common in people over the age of 50. Heredity (genetic background) and certain unusual virus infections have been suggested as causes. Thickening of involved bony areas of the lumbar spine can cause the radiating lower extremity pain of sciatica.
The only activity performed on a regular basis that fully extends the hip is walking and running. Hence as activity levels decrease so does the ability to extend the hip. This results in compensatory pelvic tilting and lumbar extension, with a reduction in the ability to accommodate uneven ground, negotiate obstacles, or attempt to change walking speed quickly. The compensatory pelvic tilt that accompanies tight hip flexors also predisposes the individual to postural problems and back pain. Hip stretches done on a regular basis can help you maintain extension range of motion and thereby improve function.
^ Enke, Oliver; New, Heather A.; New, Charles H.; Mathieson, Stephanie; McLachlan, Andrew J.; Latimer, Jane; Maher, Christopher G.; Lin, C.-W. Christine (2 July 2018). "Anticonvulsants in the treatment of low back pain and lumbar radicular pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Canadian Medical Association Journal. 190 (26): E786–E793. doi:10.1503/cmaj.171333. PMC 6028270. PMID 29970367.

Everything you need to know about osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis is a potentially painful condition that leads to inflammation, loss of cartilage, and bone damage. Read our article to find out how it happens and what treatments can help. Also, see a fully interactive 3-D model that you can explore to look inside a joint when signs of osteoarthritis begin to appear. Read now
You can use over-the-counter remedies such as Motrin or Advil (ibuprofen) or Aleve (naproxen) to help with pain and swelling. Tylenol (acetaminophen) works for pain relief, but it doesn't treat inflammation and swelling. If you have heart disease, high blood pressure, kidney disease, or if you've had ulcers or internal bleeding, check with your doctor before taking any of these medications.
Take nonprescription pain medicine, such as acetaminophen, ibuprofen, or naproxen. Read the label and take as directed. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, may cause stomach bleeding and other problems. These risks increase with age. Unless recommended by your healthcare provider, do not take an NSAID for more than 10 days.

If you’re someone who’s got a good stretching routine down, both before and after a HIIT workout, bike ride or run, odds are the discomfort you feel indicates that there are grounds for more strengthening exercises. It’s important to add that many yogis with extremely flexible hips run into overstretching injuries like hip flexor strains. But, these injuries aren’t just limited to the uber-flexible. Runners, cyclists, and Stairmaster lovers might strain these muscles due to frequent overuse. We’ll share a hip flexor workout below but, first up, some stretches.
You’d think so. But consider this story of a motorcycle accident: many years ago, a friend hit a car that had pulled out from a side street. He flew over the car & landed on his head. Bystanders showed their ignorance of spinal fracture by, yikes, carelessly moving him. In fact, his thoracic spine was significantly fractured … yet the hospital actually refused to do an X-ray because he had no obvious symptoms of a spinal fracture. Incredible! The next day, a horrified orthopedic surgeon ordered an X-ray immediately, confirming the fracture & quite possibly saved him from paralysis.
Moist heat may help relax your muscles. Put moist heat on the sore area for 10 to 15 minutes at a time before you do warm-up and stretching exercises. Moist heat includes heat patches or moist heating pads that you can buy at most drugstores, a wet washcloth or towel that has been heated in a microwave or the dryer, or a hot shower. Don’t use heat if you have swelling.

If low back pain gets worse or does not improve after two to three days of home treatment, contact a primary-care physician. The physician can evaluate the patient and perform a neurological exam in the office to determine which nerve root is being irritated, as well as rule out other serious medical conditions. If there are clear signs that the nerve root is being compressed, a physician can prescribe medications to relieve the pain, swelling and irritation; he or she also may recommend limitation of activities. If these treatment options do not provide relief within two weeks, it may be time to consider other diagnostic studies and possibly surgery.

Nerve irritation: The nerves of the lumbar spine can be irritated by mechanical pressure (impingement) by bone or other tissues, or from disease, anywhere along their paths -- from their roots at the spinal cord to the skin surface. These conditions include lumbar disc disease (radiculopathy), bony encroachment, and inflammation of the nerves caused by a viral infection (shingles). See descriptions of these conditions below.
Spinal laminectomy (also known as spinal decompression) is performed when spinal stenosis causes a narrowing of the spinal canal that causes pain, numbness, or weakness. During the procedure, the lamina or bony walls of the vertebrae, along with any bone spurs, are removed. The aim of the procedure is to open up the spinal column to remove pressure on the nerves.
Discectomy (the partial removal of a disc that is causing leg pain) can provide pain relief sooner than nonsurgical treatments.[14] Discectomy has better outcomes at one year but not at four to ten years.[14] The less invasive microdiscectomy has not been shown to result in a different outcome than regular discectomy.[14] For most other conditions, there is not enough evidence to provide recommendations for surgical options.[14] The long-term effect surgery has on degenerative disc disease is not clear.[14] Less invasive surgical options have improved recovery times, but evidence regarding effectiveness is insufficient.[14]
Prolonged sitting and activities like running or cycling can lead to tight hip flexor muscles and a variety of skeletal imbalances. Think: if you only cycle for exercise, certain muscles in your legs will get stronger (in a lot of cases you overwork these muscles) yet your core and outer hip muscles might get weaker from lack of engagement. So what? Well, these muscle imbalances often lead to skeletal imbalances and injuries down the line. If you have particularly tight hip flexors, your body will start to create an anterior pull on the pelvis (anterior pelvic tilt). You can identify an anterior pelvic tilt if your belly protrudes slightly in the front while your butt sticks out in the back (what some people refer to as “duck butt”).

Degenerative Conditions: Sometimes, degenerative conditions that are the normal result of aging may cause your low back pain. Conditions like spinal stenosis, arthritis, or degenerative disc disease can all cause pain. Congenital conditions, like spondylolisthesis or scoliosis, can also cause your back pain. For most degenerative back problems, movement and exercise have been proven to be effective in treating these conditions. A visit to your physical therapist can help you determine the correct progression of back exercises for your specific condition.
Nucleoplasty, also called plasma disc decompression (PDD), is a type of laser surgery that uses radiofrequency energy to treat people with low back pain associated with mildly herniated discs. Under x-ray guidance, a needle is inserted into the disc. A plasma laser device is then inserted into the needle and the tip is heated to 40-70 degrees Celsius, creating a field that vaporizes the tissue in the disc, reducing its size and relieving pressure on the nerves. Several channels may be made depending on how tissue needs to be removed to decompress the disc and nerve root.
An injury to a ligament is called a sprain, and an injury to muscle or tendon is called a strain. Sprains and strains may be caused by repetitive movements or a single stressful incident. Symptoms and signs include pain and swelling. Though treatment depends upon the extent and location of the injury, rest, ice, compression, and elevation are key elements of treatment.
You may hear a clicking noise when you move your hip, but that sound is not necessarily a hip flexor issue. Siegrist says the clicking isn't generally the hip flexor alone and often comes from a moving part, like the joint. "Maybe there is a loose body in the joint or loose cartilage at the edge of the hip joint that is mechanically getting irritated,” she says.

Lumbar strain (acute, chronic): A lumbar strain is a stretch injury to the ligaments, tendons, and/or muscles of the low back. The stretching incident results in microscopic tears of varying degrees in these tissues. Lumbar strain is considered one of the most common causes of low back pain. The injury can occur because of overuse, improper use, or trauma. Soft-tissue injury is commonly classified as "acute" if it has been present for days to weeks. If the strain lasts longer than three months, it is referred to as "chronic." Lumbar strain most often occurs in people in their 40s, but it can happen at any age. The condition is characterized by localized discomfort in the low back area with onset after an event that mechanically stressed the lumbar tissues. The severity of the injury ranges from mild to severe, depending on the degree of strain and resulting spasm of the muscles of the low back. The diagnosis of lumbar strain is based on the history of injury, the location of the pain, and exclusion of nervous system injury. Usually, X-ray testing is only helpful to exclude bone abnormalities.
Low back pain can cause a wide variety of symptoms and signs depending on the precise cause of the pain as reviewed above. Symptoms that can be associated with low back pain include numbness and/or tingling of the lower extremities, incontinence of urine or stool, inability to walk without worsening pain, lower extremity weakness, atrophy (decreased in size) of the lower extremity muscles, rash, fever, chills, weight loss, abdominal pains, burning on urination, dizziness, joint pain, and fatigue.
I’m not endorsing or saying these stretches are a miracle cure, but I definitely think they’ve helped. I’ve even started to add a few gentle yoga poses and pilates moves which I could so easily do, back in the day, when I was 63 kilos and participated in the greatest oxymoron ever named … a thing called the Fun Run. If I’m not careful, and I keep stretching away each day, I could end up with a 6 pack and back to my 5′ 7″ instead of 5′ 5″.
Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Place left ankle right below right knee, creating a “four” shape with left leg. Thread left arm through the opening you created with left leg and clasp hands behind right knee. Lift right foot off floor and pull right knee toward chest, flexing left foot. Hold for 30 seconds, then repeat on opposite side.
Low and lower back pain can vary from dull pain that develops gradually to sudden, sharp or persistent pain felt below the waist. Unfortunately, almost everyone, at some point during life will experience low back pain that may travel downward into the buttocks and sometimes into one or both lower extremities. The most common cause is muscle strain often related to heavy physical labor, lifting or forceful movement, bending or twisting into awkward positions, or standing in one position too long.

When I do a deep knee bend like a sumo squat I get a popping in the outside of my left knee. It feels like a big tendon or ligament is slipping per something. It isn’t painful peer se but I’m afraid if I do it a lot it will be. Is that a relatively common symptom for a guy with tight flexors, it bands, etc? Should I just push through it or have it checked out?
To understand various causes of low back pain, it is important to appreciate the normal design (anatomy) of the tissues of this area of the body. Important structures of the low back that can be related to symptoms in this region include the bony lumbar spine (vertebrae, singular = vertebra), discs between the vertebrae, ligaments around the spine and discs, spinal cord and nerves, muscles of the low back, internal organs of the pelvis and abdomen, and the skin covering the lumbar area.
This standard recommendation reinforces the alarming idea that low back pain that lasts longer than a few weeks is Really Bad News. It’s not. It’s a clue. It’s a reason for concern and alertness. But many cases of low back pain that last for 6 weeks will still go away. Once again, see the 2009 research published in the British Medical Journal, which showed that more than 30% of patients with “new” chronic low back pain will still recover without treatment. BACK TO TEXT
Iliopsoas syndrome, which is also called psoas syndrome or iliopsoas tendonitis, occurs when the iliopsoas muscles are injured. Lower back pain is the most common symptom; however, pain can also occur in the hip, thigh, or leg. The iliopsoas bursa, which is a fluid-filled sac located on the inside of the hip that reduces rubbing and friction, is also likely to become inflamed due to the proximity of the two structures. When this happens, the inflamed bursae will make it difficult to move.
Bone scans are used to detect and monitor infection, fracture, or disorders in the bone. A small amount of radioactive material is injected into the bloodstream and will collect in the bones, particularly in areas with some abnormality. Scanner-generated images can be used to identify specific areas of irregular bone metabolism or abnormal blood flow, as well as to measure levels of joint disease.
Flexors are flexible muscle tissues that help a person stretch and move. The muscles that help you lift your knee toward your body and bend at the waist are known as the hip flexors. These muscles are located around the upper and inner things and pelvic region. Keeping the hip flexors strong is particularly important for active people and athletes.
Spinal laminectomy (also known as spinal decompression) is performed when spinal stenosis causes a narrowing of the spinal canal that causes pain, numbness, or weakness. During the procedure, the lamina or bony walls of the vertebrae, along with any bone spurs, are removed. The aim of the procedure is to open up the spinal column to remove pressure on the nerves.
If you have hip arthritis, work on building up the muscles in your outer thigh for added support. Lie on your pain-free side and lift the leg with arthritis up about six inches, hold for two or three seconds, and lower it again, Humphrey says. Start with one set of 10 repetitions and build up to three sets. Repeat on the other side unless it is too painful. This exercise can aggravate your symptoms if you have hip pain from bursitis.
THIS TOOL DOES NOT PROVIDE MEDICAL ADVICE. It is intended for general informational purposes only and does not address individual circumstances. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment and should not be relied on to make decisions about your health. Never ignore professional medical advice in seeking treatment because of something you have read on the WebMD Site. If you think you may have a medical emergency, immediately call your doctor or dial 911.
"Lower back pain is the most common musculoskeletal ailment in the U.S., and can often be mitigated by strengthening the core musculature," Blake Dircksen, D.P.T., C.S.C.S., a physical therapist at Bespoke Treatments New York, tells SELF. "The 'core' is a cylinder of abdominal and back muscles that wraps around the body like a corset," Dircksen explains. (The glutes are also considered a part of the core, since they connect to the pelvis and ultimately the back and abdominal muscles.) As with any muscles, by strengthening them, you will increase the amount of weight your lower back can comfortably move, which means it will be better equipped to handle the same stress from your workouts and everyday life without getting as achey.
"Lower back pain is the most common musculoskeletal ailment in the U.S., and can often be mitigated by strengthening the core musculature," Blake Dircksen, D.P.T., C.S.C.S., a physical therapist at Bespoke Treatments New York, tells SELF. "The 'core' is a cylinder of abdominal and back muscles that wraps around the body like a corset," Dircksen explains. (The glutes are also considered a part of the core, since they connect to the pelvis and ultimately the back and abdominal muscles.) As with any muscles, by strengthening them, you will increase the amount of weight your lower back can comfortably move, which means it will be better equipped to handle the same stress from your workouts and everyday life without getting as achey.
Example: a friend of mine went to the hospital after a motorcycle accident. He’d flown over a car and landed hard on his head. Bizarrely, he was sent home with very little care, and no imaging of his back, even though he was complaining of severe lower back pain. A doctor reassured him that it was just muscle spasms. (This all happened at a hospital that was notorious for being over-crowded and poorly run.) The next day, still in agony, he went to see a doctor at a walk-in clinic, who immediately took him for an x-ray … which identified a serious lumbar fracture and imminent danger of paralysis. He had been lucky to get through the night without disaster! He was placed on a spine board immediately and sent for surgery. The moral of the story? Sometimes, when you’ve had a major trauma and your back really hurts, it’s because your back is broken. BACK TO TEXT
Lumbar radiculopathy: Lumbar radiculopathy is nerve irritation that is caused by damage to the discs between the vertebrae. Damage to the disc occurs because of degeneration ("wear and tear") of the outer ring of the disc, traumatic injury, or both. As a result, the central softer portion of the disc can rupture (herniate) through the outer ring of the disc and abut the spinal cord or its nerves as they exit the bony spinal column. This rupture is what causes the commonly recognized "sciatica" pain of a herniated disc that shoots from the low back and buttock down the leg. Sciatica can be preceded by a history of localized low-back aching or it can follow a "popping" sensation and be accompanied by numbness and tingling. The pain commonly increases with movements at the waist and can increase with coughing or sneezing. In more severe instances, sciatica can be accompanied by incontinence of the bladder and/or bowels. The sciatica of lumbar radiculopathy typically affects only one side of the body, such as the left side or right side, and not both. Lumbar radiculopathy is suspected based on the above symptoms. Increased radiating pain when the lower extremity is lifted supports the diagnosis. Nerve testing (EMG/electromyogramspina bifida
Here is how you do the hip rotation stretch: Sit on the floor with your knee out straight. Cross one leg over the other by placing your ankle on top of your knee (as if crossing your legs while sitting). Gently pull your knee across your body, and hold for five seconds. Then gently push the knee of the top leg away from you until a stretch is felt in your hip. Hold this position for five seconds, then slowly release. Repeat 10 times.
Prolonged sitting and activities like running or cycling can lead to tight hip flexor muscles and a variety of skeletal imbalances. Think: if you only cycle for exercise, certain muscles in your legs will get stronger (in a lot of cases you overwork these muscles) yet your core and outer hip muscles might get weaker from lack of engagement. So what? Well, these muscle imbalances often lead to skeletal imbalances and injuries down the line. If you have particularly tight hip flexors, your body will start to create an anterior pull on the pelvis (anterior pelvic tilt). You can identify an anterior pelvic tilt if your belly protrudes slightly in the front while your butt sticks out in the back (what some people refer to as “duck butt”).
Along with these exercises, it's also important to do some supplementary exercises to work your hip's supporting muscles. You've probably heard of your shoulder's rotator cuff. Well, your hip also has a cuff, or a group of muscles that help stabilize and support movement. For these exercises, you'll need a mini-band, a longer thera-band or tubing (both are sold at many sporting goods stores, or can be purchased online), and a cable-column unit.
Take nonprescription pain medicine, such as acetaminophen, ibuprofen, or naproxen. Read the label and take as directed. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, may cause stomach bleeding and other problems. These risks increase with age. Unless recommended by your healthcare provider, do not take an NSAID for more than 10 days.
A healthy diet is important for a number of reasons when you have lower back pain. First, eating well can help you maintain a healthy weight. Excess weight puts extra strain on your lower back, adding to your pain. Second, a diet that’s high in key nutrients can help promote bone growth and keep your bones strong. These must-have nutrients include:

But how can you tell? It can be tricky. This is a concise, readable guide to symptoms that need better-safe-than-sorry investigation with your doctor. (It’s basically just a plain English version of clinical guidelines for doctors.9) In other words, this article explains the difference between “dangerous” and “just painful” as clearly as possible. Tables, checklists, and examples ahead.
Health care professionals diagnose hip pain with a history and physical examination. Physical examination maneuvers, such as internally and externally rotating the hip, can be used to detect pain-aggravating positions. Tenderness can be elicited by palpating over inflamed areas. Straight leg raising can detect signs of sciatica. A health care professional may use imaging studies, including X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans, to further define the causes of hip pain. Sometimes, nuclear medicine bone scans are used to image inflamed or fractured bone.
Why is back pain still a huge problem? Maybe this: “It is extremely difficult to alter the potentially disabling belief among the lay public that low back pain has a structural mechanical cause. An important reason for this is that this belief continues to be regularly reinforced by the conditions of care of a range of ‘hands-on’ providers, for whom idiosyncratic variations of that view are fundamental to their professional existence.”


