NINDS health-related material is provided for information purposes only and does not necessarily represent endorsement by or an official position of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke or any other Federal agency. Advice on the treatment or care of an individual patient should be obtained through consultation with a physician who has examined that patient or is familiar with that patient's medical history.
The bones of the hip are supported by specific muscles. The strongest muscle in the body is actually one of the main flexors of the hip, it is called the iliopsoas muscle. It has two attachments to the inner part of the hip as well as the lower part of the back. This muscle is involved in iliopsoas tendinitis, iliopsoas bursitis, and is one of the most common causes of muscle pain that causes hip pain. The tendons attach the muscles to the bones and the ligaments attach bone to bone. Areas that are often susceptible to increased pressure are the tendons or the muscles attached to the bone, so that is another source of pain in iliopsoas tendinitis. The bursa are pockets of fluid that also protect the top part of the bone to prevent pressure on the bone. There are about 160 bursa in the body, and when they get irritated, it can develop into bursitis.
^ Jump up to: a b c d e f Qaseem, A; Wilt, TJ; McLean, RM; Forciea, MA; Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of, Physicians. (4 April 2017). "Noninvasive Treatments for Acute, Subacute, and Chronic Low Back Pain: A Clinical Practice Guideline From the American College of Physicians". Annals of Internal Medicine. 166 (7): 514–530. doi:10.7326/M16-2367. PMID 28192789.
Before recommending exercises, physical therapists evaluate their patients to develop a routine that’s appropriate for their specific condition. Pariser says the following exercises, done at home and at the gym, are generally safe for everyone. “If a patient has already received a total hip replacement, however, certain precautions should be taken,” he says.

Treatment options include physical therapy, back exercises, weight reduction, steroid injections (epidural steroids), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, rehabilitation and limited activity. All of these treatment options are aimed at relieving the inflammation in the back and irritation of nerve roots. Physicians usually recommend four to six weeks of conservative therapy before considering surgery.

This stretch gets at the piriformis muscle of the hip flexor. Sit with both legs extended in front of you. Bend the right knee and place the right foot on the floor. Place your right hand behind you and hook your left elbow on the outside of the right knee. As you twist toward the righthand side, keep your spine straight and breathe deeply. Switch sides after about 20 seconds.
However, even the things you do every day — like sitting in front of a computer or at a desk for hours — can both weaken and shorten (tighten) your hip flexors, making them more prone to injury. Because of this, exercises (such as squats) and targeted stretches which focus on strengthening the hip muscles and improving hip mobility are key to preventing injuries.
Lay on your back on your mat and pull your knees to your chest. Place your hands on the inside arches of your feet and open your knees wider than shoulder-width apart. Keeping your back pressed into the mat as much as possible, press your feet into hands while pulling down on feet, creating resistance. Breathe deeply and hold for at least 30 seconds.
Nerve irritation: The nerves of the lumbar spine can be irritated by mechanical pressure (impingement) by bone or other tissues, or from disease, anywhere along their paths -- from their roots at the spinal cord to the skin surface. These conditions include lumbar disc disease (radiculopathy), bony encroachment, and inflammation of the nerves caused by a viral infection (shingles). See descriptions of these conditions below.
Lie on your back with your knees bent and your feet flat on the floor. Tighten the muscles in your buttocks, then lift your hips off the ground and hold for about five seconds before slowly lowering yourself back down. Be sure to breathe throughout the exercise. As with the first exercise, you can work up to doing 30 repetitions, resting for a few seconds (or longer) between each. “If you start to get tired, stop and rest for a couple of minutes,” Pariser says.
Emerging technologies such as X-rays gave physicians new diagnostic tools, revealing the intervertebral disc as a source for back pain in some cases. In 1938, orthopedic surgeon Joseph S. Barr reported on cases of disc-related sciatica improved or cured with back surgery.[100] As a result of this work, in the 1940s, the vertebral disc model of low back pain took over,[99] dominating the literature through the 1980s, aiding further by the rise of new imaging technologies such as CT and MRI.[100] The discussion subsided as research showed disc problems to be a relatively uncommon cause of the pain. Since then, physicians have come to realize that it is unlikely that a specific cause for low back pain can be identified in many cases and question the need to find one at all as most of the time symptoms resolve within 6 to 12 weeks regardless of treatment.[99] 
Sciatica is a form of radiculopathy caused by compression of the sciatic nerve, the large nerve that travels through the buttocks and extends down the back of the leg. This compression causes shock-like or burning low back pain combined with pain through the buttocks and down one leg, occasionally reaching the foot. In the most extreme cases, when the nerve is pinched between the disc and the adjacent bone, the symptoms may involve not only pain, but numbness and muscle weakness in the leg because of interrupted nerve signaling. The condition may also be caused by a tumor or cyst that presses on the sciatic nerve or its roots.

Bridge: Still lying on your back with your feet flat on floor, lift your hips and torso off the floor into a bridge. Then interlace your hands underneath your hips and press your shoulders and upper arms into the floor, lifting your hips higher. Hold for 10 seconds. Lower yourself slowly back down, rolling down from the top of your spine to your tailbone. Repeat three times.
First and foremost, stop slouching. One of the most common causes of low back pain is poor sitting posture. The strain on the back while sitting in a slouched position can cause excessive pressure on the joints, muscles, and discs, causing pain. Learn to sit with correct posture and maintain that posture at all times to help decrease or eliminate your low back pain. Also be sure your workspace is set up properly at home and at work.
Treatment options include physical therapy, back exercises, weight reduction, steroid injections (epidural steroids), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, rehabilitation and limited activity. All of these treatment options are aimed at relieving the inflammation in the back and irritation of nerve roots. Physicians usually recommend four to six weeks of conservative therapy before considering surgery.
When hip pain comes from muscles, tendons, or ligament injuries, it typically come from overuse syndromes. This can come from overusing the strongest hip muscles in the body such as iliopsoas tendinitis; it can come from tendon and ligament irritations, which typically are involved in snapping hip syndrome. It can come from within the joint, which is more characteristic of hip osteoarthritis. Each of these types of pain present in slightly different ways, which is then the most important part in diagnosing what the cause is by doing a good physical examination.
Poor Sitting Posture: The correct position of your low back should have a slight forward curve called a lordosis. When you sit slouched, this lordosis straightens out-or even worse-reverses itself. This loss of the forward curve in your spine can cause increased pressure on the small shock absorbing discs in your back. This increased pressure can displace your discs and lead to low back pain. Your physical therapist can teach you the proper way to sit to decrease, eliminate, or prevent your back pain.
Meanwhile, many non-dangerous problems can cause amazingly severe back pain. A muscle cramp is a good analogy — just think about how painful a Charley horse is! Regardless of what’s actually going on in there, muscle pain is probably the main thing that back pain patients are feeling. The phenomenon of trigger points — tiny muscle cramps, basically11 — could be the entire problem, or a complication that’s more painful and persistent than the original problem. It’s hard to overstate how painful trigger points can be, but they are not dangerous to anything but your comfort.
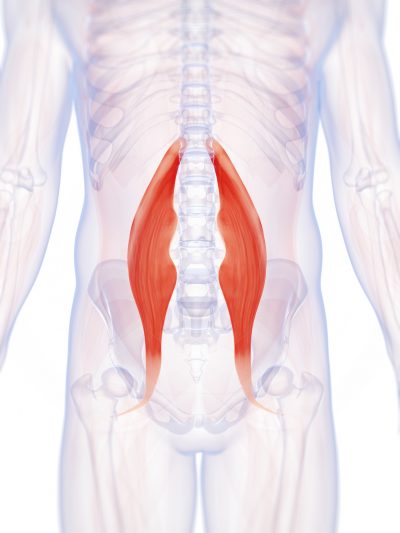
The iliopsoas muscles are a group of two muscles—the psoas muscle and the iliacus muscle—located toward the front of the inner hip. The psoas muscles, in particular, is located in the lumbar (lower) region of the spine and extends through the pelvis to the femur. The iliopsoas muscles are the primary hip flexors, pulling the knee up off the ground when it contracts. Because the psoas muscle is also connected to the spine, it contributes to upright posture, assists in lumbar spine movement, and influences the spine’s curve.
Grade III (severe): A complete tear in your muscle that causes severe pain and swelling and you can't bear weight on that leg, making it difficult to walk. You've also lost more than 50 percent of your muscle function. These injuries are less common and may need surgery to repair the torn muscle. They can take several months or more to completely heal.

Strengthening exercises, beyond general daily activities, are not advised for acute low back pain, but may be an effective way to speed recovery from chronic or subacute low back pain. Maintaining and building muscle strength is particularly important for persons with skeletal irregularities. Health care providers can provide a list of beneficial exercises that will help improve coordination and develop proper posture and muscle balance. Evidence supports short- and long-term benefits of yoga to ease chronic low back pain.
Work on strengthening all of your core muscles and glutes. These muscles work together to give you balance and stability and to help you move through the activities involved in daily living, as well as exercise and sports. When one set of these muscles is weak or tight, it can cause injury or pain in another, so make sure you pay equal attention to all of them.
Exercise appears to be useful for preventing low back pain.[47] Exercise is also probably effective in preventing recurrences in those with pain that has lasted more than six weeks.[1][48] Medium-firm mattresses are more beneficial for chronic pain than firm mattresses.[49] There is little to no evidence that back belts are any more helpful in preventing low back pain than education about proper lifting techniques.[47][50] Shoe insoles do not help prevent low back pain.[47][51]
How to: Lie on your back with your right knee bent and foot flat on the floor (a). Extend your left leg up to the ceiling and wrap a strap around the sole of your left foot (b). While holding both ends with your left hand, extend your right arm directly out to the side in order to anchor yourself (c). Slowly let the left leg fall toward the left while keeping your right side grounded. Hold for six to eight breaths, then repeat on the opposite side.
The hip is a common site of osteoarthritis. To help protect the hip joint from "wear and tear," it is important to strengthen the muscles that support it. Your hip also controls the position of your knee, and strengthening your hips may be one component of your rehab program for knee pain. Your physical therapist may also prescribe hip exercises after total hip replacement if you have a hip labrum tear or as part of your hip exercise program for hip pain.
There are a number of ways to classify low back pain with no consensus that any one method is best.[5] There are three general types of low back pain by cause: mechanical back pain (including nonspecific musculoskeletal strains, herniated discs, compressed nerve roots, degenerative discs or joint disease, and broken vertebra), non-mechanical back pain (tumors, inflammatory conditions such as spondyloarthritis, and infections), and referred pain from internal organs (gallbladder disease, kidney stones, kidney infections, and aortic aneurysm, among others).[5] Mechanical or musculoskeletal problems underlie most cases (around 90% or more),[5][34] and of those, most (around 75%) do not have a specific cause identified, but are thought to be due to muscle strain or injury to ligaments.[5][34] Rarely, complaints of low back pain result from systemic or psychological problems, such as fibromyalgia and somatoform disorders.[34]
Physician specialties that evaluate and treat low back pain range from generalists to subspecialists.These specialties include emergency medicine physicians, general medicine, family medicine, internal medicine, gynecology, spine surgeons (orthopaedics and neurosurgery), rheumatology, pain management, and physiatry. Other health care providers for low back pain include physical therapists, chiropractors, massage therapists, psychologists, and acupuncturists.
The hip is a very stable ball and socket type joint with an inherently large range of motion. The hip contains some of the largest muscle in the body as well as some of the smallest. Most people lack mobility due to a relatively sedentary lifestyle. Periods of prolonged sitting results in tightness of the hip flexors and hamstrings. Tightness in the muscles and ligaments can created joint forces that result in arthritis, postural problems, bursitis, and mechanical back pain.
An intervertebral disc has a gelatinous core surrounded by a fibrous ring.[32] When in its normal, uninjured state, most of the disc is not served by either the circulatory or nervous systems – blood and nerves only run to the outside of the disc.[32] Specialized cells that can survive without direct blood supply are in the inside of the disc.[32] Over time, the discs lose flexibility and the ability to absorb physical forces.[25] This decreased ability to handle physical forces increases stresses on other parts of the spine, causing the ligaments of the spine to thicken and bony growths to develop on the vertebrae.[25] As a result, there is less space through which the spinal cord and nerve roots may pass.[25] When a disc degenerates as a result of injury or disease, the makeup of a disc changes: blood vessels and nerves may grow into its interior and/or herniated disc material can push directly on a nerve root.[32] Any of these changes may result in back pain.[32]
How to do it: Stand with your feet together, holding dumbbells by your sides. Take a wide step out to your right and lower into a side lunge, reaching dumbbells on either side of right leg [as shown]. Bend your left knee and shift your weight into both legs, into a wide squat position, reaching the dumbbells to floor in front of you, then extend your right leg and shift your weight to the left, moving into a side lunge with your left leg.
You're more likely to get a hip flexor injury if you've had one in the past, you don't warm up properly before engaging in athletic activity, your muscles are already tight or stiff, or your muscles are weak from being overused. If, while exercising, you try to do too much at once in too short an amount of time, you can also put yourself at risk for a hip flexor injury.
You’d think so. But consider this story of a motorcycle accident: many years ago, a friend hit a car that had pulled out from a side street. He flew over the car & landed on his head. Bystanders showed their ignorance of spinal fracture by, yikes, carelessly moving him. In fact, his thoracic spine was significantly fractured … yet the hospital actually refused to do an X-ray because he had no obvious symptoms of a spinal fracture. Incredible! The next day, a horrified orthopedic surgeon ordered an X-ray immediately, confirming the fracture & quite possibly saved him from paralysis.
However, even the things you do every day — like sitting in front of a computer or at a desk for hours — can both weaken and shorten (tighten) your hip flexors, making them more prone to injury. Because of this, exercises (such as squats) and targeted stretches which focus on strengthening the hip muscles and improving hip mobility are key to preventing injuries.
Pain is generally an unpleasant feeling in response to an event that either damages or can potentially damage the body's tissues. There are four main steps in the process of feeling pain: transduction, transmission, perception, and modulation.[12] The nerve cells that detect pain have cell bodies located in the dorsal root ganglia and fibers that transmit these signals to the spinal cord.[33] The process of pain sensation starts when the pain-causing event triggers the endings of appropriate sensory nerve cells. This type of cell converts the event into an electrical signal by transduction. Several different types of nerve fibers carry out the transmission of the electrical signal from the transducing cell to the posterior horn of spinal cord, from there to the brain stem, and then from the brain stem to the various parts of the brain such as the thalamus and the limbic system. In the brain, the pain signals are processed and given context in the process of pain perception. Through modulation, the brain can modify the sending of further nerve impulses by decreasing or increasing the release of neurotransmitters.[12]
Talmage, J; Belcourt, R; Galper, J; et al. (2011). "Low back disorders". In Kurt T. Hegmann. Occupational medicine practice guidelines : evaluation and management of common health problems and functional recovery in workers (3rd ed.). Elk Grove Village, IL: American College of Occupational and Environmental Medicine. pp. 336, 373, 376–377. ISBN 978-0615452272.

How to: Lie on your back with your right knee bent and foot flat on the floor (a). With your left leg fully extended, press into your right foot to shift onto your left hip. This is your starting position (b). Then, squeeze your right glutes to press your left hip open until you feel a stretch, pause, then return to start. That’s one rep (c). Perform six to eight reps, then repeat on the opposite side.

Sciatica is a form of radiculopathy caused by compression of the sciatic nerve, the large nerve that travels through the buttocks and extends down the back of the leg. This compression causes shock-like or burning low back pain combined with pain through the buttocks and down one leg, occasionally reaching the foot. In the most extreme cases, when the nerve is pinched between the disc and the adjacent bone, the symptoms may involve not only pain, but numbness and muscle weakness in the leg because of interrupted nerve signaling. The condition may also be caused by a tumor or cyst that presses on the sciatic nerve or its roots.
The iliotibial band is a thickening of the fascia lata, the deep fascia of the thigh. Think of it as a thick long ligament like structure that connects the hip to the lower leg along the outside of the thigh. Tightness in the iliotibial band can cause patellofemoral pain, trochanteric bursitis, and friction syndromes at the knee. This is a hip stretch I commonly prescribe to runners and people suffering from knee pain.
Medications: A wide range of medications are used to treat acute and chronic low back pain. Some are available over the counter (OTC); others require a physician’s prescription. Certain drugs, even those available OTC, may be unsafe during pregnancy, may interact with other medications, cause side effects, or lead to serious adverse effects such as liver damage or gastrointestinal ulcers and bleeding. Consultation with a health care provider is advised before use. The following are the main types of medications used for low back pain:

“Red flags” are signs or symptoms that something medically ominous may be going on. Red flags are not reliable, and their presence is not a diagnosis. When you have some red flags, it only indicates a need to look more closely. Sometimes red flags are missing there really is something serious going on … and sometimes they are a false alarm.18 Check off all that apply … hopefully none or few or only the least alarming of them!
Low back pain has been with humans since at least the Bronze Age. The oldest known surgical treatise – the Edwin Smith Papyrus, dating to about 1500 BCE – describes a diagnostic test and treatment for a vertebral sprain. Hippocrates (c. 460 BCE – c. 370 BCE) was the first to use a term for sciatic pain and low back pain; Galen (active mid to late second century CE) described the concept in some detail. Physicians through the end of the first millennium did not attempt back surgery and recommended watchful waiting. Through the Medieval period, folk medicine practitioners provided treatments for back pain based on the belief that it was caused by spirits.[99]
How to do it: Stand with your feet together, holding dumbbells by your sides. Take a wide step out to your right and lower into a side lunge, reaching dumbbells on either side of right leg [as shown]. Bend your left knee and shift your weight into both legs, into a wide squat position, reaching the dumbbells to floor in front of you, then extend your right leg and shift your weight to the left, moving into a side lunge with your left leg.
^ Chou R, Loeser JD, Owens DK, Rosenquist RW, Atlas SJ, Baisden J, Carragee EJ, Grabois M, Murphy DR, Resnick DK, Stanos SP, Shaffer WO, Wall EM, American Pain Society Low Back Pain Guideline Panel (2009). "Interventional therapies, surgery, and interdisciplinary rehabilitation for low back pain: An evidence-based clinical practice guideline from the American Pain Society". Spine. 34 (10): 1066–77. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181a1390d. PMID 19363457.

^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g Hughes SP, Freemont AJ, Hukins DW, McGregor AH, Roberts S (October 2012). "The pathogenesis of degeneration of the intervertebral disc and emerging therapies in the management of back pain" (PDF). J Bone Joint Surg Br. 94 (10): 1298–304. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.94B10.28986. PMID 23015552. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 October 2013. Retrieved 25 June 2013.

Imagine not being able to climb stairs, bend over, or even walk Changes in hip joint muscle-tendon lengths with mode of locomotion. Riley, P.O., Franz, J., Dicharry, J., et al. Center for Applied Biomechanics, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA. Gait & Posture, 2010 Feb; 31 (2): 279-83.. All pretty essential if you ask us! But that’s what our bodies would be like without our hip flexor muscles. Never heard of ‘em? It’s about time we share why they’re so important, how your desk job might be making them weaker (ah!), and the best ways to stretch them out.
Icing a joint that’s inflamed because of arthritis or bursitis can lower inflammation and help with hip pain. “If it’s very painful, I sometimes tell patients to ice four or five times daily for about 10 to 15 minutes,” says Amy Humphrey, DPT, a physical therapist at Body Dynamics, Inc. in Arlington, Va. Use an ice pack, wrap a towel around it, and put it where you feel the pain.

Stop listening to other people’s horror stories. You know the scenario: You are bent over in obvious pain, waiting to see the doctor, and the person next to you tells you a 10-minute tale of how their Uncle Gordon had low back pain that required injections and surgery. But the pain still didn’t go away. Stop listening to these terrible stories. Most low back pain is short-lived and can be managed quite effectively with exercise and postural correction. Of course, some low back conditions are serious and require surgery, but that is a conversation you should have with your doctor, not the guy in the waiting room.

There are many tendons located around the hip that connect the muscles to the joint. With various activities or overuse, these tendons can become inflamed. This inflammation results in pain around the hip region. Iliotibial band syndrome is one of the most common causes of tendonitis at the hip joint. The hallmark of this condition is pain on the lateral, or outside, aspect of your hip.
Doing the bridge exercise in the morning gets your muscles working, activated, and engaged and will help support you the rest of the day, says Humphrey. Lie on your back with your legs bent and your feet flat on the floor, hip-width apart. Press down through your ankles and raise your buttocks off the floor while you tighten your abdominal muscles. Keep your knees aligned with your ankles and aim for a straight line from knees to shoulders, being sure not to arch your back; hold this position for three to five seconds and then slowly lower your buttocks back to the floor. Start with one set of 10 and build up to two or three sets.

Really a great content. Let me tell you first about hip flexor it is the engine through which our body moves. They control balance, our ability to sit, stand, twist, reach, bend, walk and step. One of my patient also suffering from same problem but due to lack of money he was unable to afford a treatment. So i recommend him a program to unlock hip flexor. If anyone wants they can check it out here ;- https://tinyurl.com/y8yaqs2s Report