3. Tendinitis and bursitis Many tendons around the hip connect the muscles to the joint. These tendons can easily become inflamed if you overuse them or participate in strenuous activities. One of the most common causes of tendinitis at the hip joint, especially in runners, is iliotibial band syndrome — the iliotibial band is the thick span of tissue that runs from the outer rim of your pelvis to the outside of your knee.
Spondylolisthesis. This condition occurs when one vertebra slips over the adjacent one. There are 5 types of spondylolisthesis but the most common are secondary to a defect or fracture of the pars (between the facet joints) or mechanical instability of the facet joints (degenerative). The pain can be caused by instability (back) or compression of the nerves (leg).
Moist heat may help relax your muscles. Put moist heat on the sore area for 10 to 15 minutes at a time before you do warm-up and stretching exercises. Moist heat includes heat patches or moist heating pads that you can buy at most drugstores, a wet washcloth or towel that has been heated in a microwave or the dryer, or a hot shower. Don’t use heat if you have swelling.

Health Tools Baby Due Date CalculatorBasal Metabolic Rate CalculatorBody Mass Index (BMI) CalculatorCalories Burned CalculatorChild Energy Requirements CalculatorDaily Calcium Requirements CalculatorDaily Fibre Requirements CalculatorIdeal Weight CalculatorInfectious Diseases Exclusion Periods ToolOvulation CalculatorSmoking Cost CalculatorTarget Heart Rate CalculatorWaist-to-hip Ratio Calculator Risk Tests Depression Self-AssessmentErectile Dysfunction ToolMacular Degeneration ToolOsteoporosis Risk TestProstate Symptoms Self-Assessment
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) relieve pain and inflammation and include OTC formulations (ibuprofen, ketoprofen, and naproxen sodium). Several others, including a type of NSAID called COX-2 inhibitors, are available only by prescription. Long-term use of NSAIDs has been associated with stomach irritation, ulcers, heartburn, diarrhea, fluid retention, and in rare cases, kidney dysfunction and cardiovascular disease. The longer a person uses NSAIDs the more likely they are to develop side effects. Many other drugs cannot be taken at the same time a person is treated with NSAIDs because they alter the way the body processes or eliminates other medications.
Antidepressants may be effective for treating chronic pain associated with symptoms of depression, but they have a risk of side effects.[13] Although the antiseizure drugs gabapentin, pregabalin, and topiramate are sometimes used for chronic low back pain evidence does not support a benefit.[79] Systemic oral steroids have not been shown to be useful in low back pain.[1][13] Facet joint injections and steroid injections into the discs have not been found to be effective in those with persistent, non-radiating pain; however, they may be considered for those with persistent sciatic pain.[80] Epidural corticosteroid injections provide a slight and questionable short-term improvement in those with sciatica but are of no long term benefit.[81] There are also concerns of potential side effects.[82]
Disk tear. Small tears to the outer part of the disk (annulus) sometimes occur with aging. Some people with disk tears have no pain at all. Others can have pain that lasts for weeks, months, or even longer. A small number of people may develop constant pain that lasts for years and is quite disabling. Why some people have pain and others do not is not well understood.
Athletes are at greater risk of sustaining a lumber spine injury due to physical activity. Whether the sport is skiing, basketball, football, gymnastics, soccer, running, golf, or tennis-the spine undergoes a lot of stress, absorption of pressure, twisting, turning, and even bodily impact. This strenuous activity puts stress on the back that can cause injury to even the finest and most fit athletes.

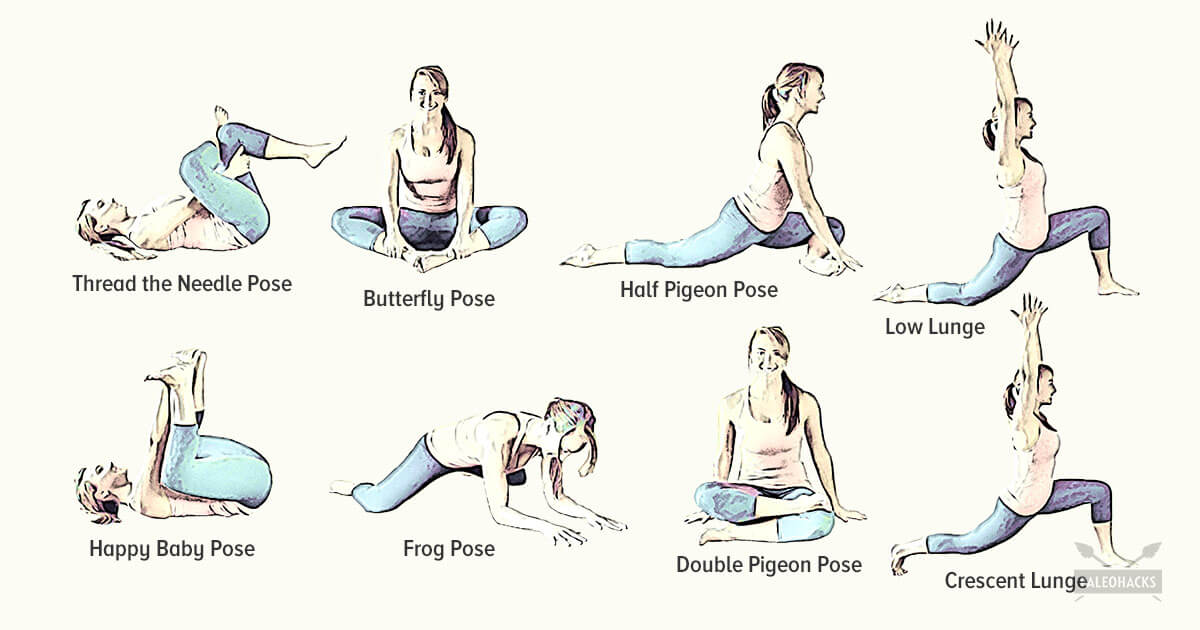
To help you strengthen these important muscles, Miranda put together a list of exercises, below. They include dynamic warm-up moves, meant to activate your hip muscles and prep them for the bigger movements to come; functional moves that train basic movement patterns, like the squat, hip hinge, and lunge; functional plyometric exercises that train explosive power; and a few moves that get you moving in different planes of motion, or directions.
Sciatica is a form of radiculopathy caused by compression of the sciatic nerve, the large nerve that travels through the buttocks and extends down the back of the leg. This compression causes shock-like or burning low back pain combined with pain through the buttocks and down one leg, occasionally reaching the foot. In the most extreme cases, when the nerve is pinched between the disc and the adjacent bone, the symptoms may involve not only pain, but numbness and muscle weakness in the leg because of interrupted nerve signaling. The condition may also be caused by a tumor or cyst that presses on the sciatic nerve or its roots.
Recurring back pain resulting from improper body mechanics is often preventable by avoiding movements that jolt or strain the back, maintaining correct posture, and lifting objects properly. Many work-related injuries are caused or aggravated by stressors such as heavy lifting, contact stress (repeated or constant contact between soft body tissue and a hard or sharp object), vibration, repetitive motion, and awkward posture. Using ergonomically designed furniture and equipment to protect the body from injury at home and in the workplace may reduce the risk of back injury.
Beacon Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine, Ltd. complies with applicable Federal civil rights laws and does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, age, disability, or sex. If you speak a language other than English, language assistance services, free of charge, are available to you. Call the Call Center at (513) 354-3700. Español (Spanish): ATENCIÓN: Si habla español, tiene a su disposición servicios gratuitos de asistencia lingüística. Llame al Call Center at (513) 354-3700. 繁體中文 (Chinese): 注意:如果您使用繁體中文,您可以免費獲得語言援助服務。請致電 Call Center at (513) 354-3700.
Whether you lift heavy items for your job or simply have a slipped disk from a pesky athletic injury, lower back pain is likely to plague you at some point in your life. Low back pain can result from an acute injury or from chronic overuse that leads to arthritis. This, in turn, can break down the fluid-filled disks in your spine that act as shock absorbers. Whatever the cause, there are some practices you can do to strengthen your back and keep lower back pain at bay.
Tight hip flexors can result in lower back pain, hip pain and injury. A lot of strain is put on those muscles during activities that involve sprinting and kicking. For example, runners are more prone to hip flexor injuries because of the small, repetitive movement during running. But even if you’re not an athlete, hip flexor injuries can occur during everyday activities (for instance, slipping and falling or running to catch a bus). When those tight muscles are suddenly stretched beyond what they are accustomed to, you might also experience pain in the upper groin region, typically where the hip meets the pelvis. 
A sedentary lifestyle can lead to having weak and tight hip flexors as they are always in the shortened position. Tight hip flexors can lead to a limited range of motion, poor posture, lower back, and hip pain, and even injuries. These muscles need to get a workout when you are standing and doing movements such as raising your leg to climb stairs, run, or ride a bicycle.


