The condition is cauda equina syndrome. It involves “acute loss of function of the neurologic elements (nerve roots) of the spinal canal below the termination (conus) of the spinal cord,” where the nerves spread out like a horse (equina) tail. Again, this condition causes symptoms in the “saddle” of the body: butt, groin, inner thighs. BACK TO TEXT
The outlook for low back pain absolutely depends on its precise cause. For example, acute strain injuries generally heal entirely with minimal treatment. On the other hand, bony abnormalities that are irritating the spinal cord can require significant surgical repair and the outlook depends on the surgical result. Long-term optimal results often involve exercise rehabilitation programs that can involve physical therapists.
Doing the bridge exercise in the morning gets your muscles working, activated, and engaged and will help support you the rest of the day, says Humphrey. Lie on your back with your legs bent and your feet flat on the floor, hip-width apart. Press down through your ankles and raise your buttocks off the floor while you tighten your abdominal muscles. Keep your knees aligned with your ankles and aim for a straight line from knees to shoulders, being sure not to arch your back; hold this position for three to five seconds and then slowly lower your buttocks back to the floor. Start with one set of 10 and build up to two or three sets.

Keeping your hips mobile is important for overall hip function and athletic performance. Mobility refers to the ability of your joints to move through a pain-free, unrestricted range of motion. For cyclists, hip mobility is critical since pedaling occurs in one plane of motion, and after miles and miles in the saddle, hip tightness and restriction may develop. The following movements will help with hip mobility.
When was the last time you got on your gym's abductor or adductor machine and got in a good workout? It's probably been a while. Both are machines that don't get a lot of use, and they are often the target of coaches' ridicule on those "useless gym moves we should all skip" lists. Perhaps rightly so, especially if you're hopping on those machines hoping for a slimming effect.
If you’re worried you’re headed toward a surgeon’s office, there might be hope. According to the Arthritis Foundation, the best way to avoid hip replacement surgery is to get active in an exercise program. In a study, people who participated in an exercise program for 12 weeks were 44 percent less likely to need joint-replacement surgery six years later than those who did not exercise.
Complaints of low back pain are one of the most common reasons people visit doctors.[9][42] For pain that has lasted only a few weeks, the pain is likely to subside on its own.[43] Thus, if a person's medical history and physical examination do not suggest a specific disease as the cause, medical societies advise against imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs.[42] Individuals may want such tests but, unless red flags are present,[10][44] they are unnecessary health care.[9][43] Routine imaging increases costs, is associated with higher rates of surgery with no overall benefit,[45][46] and the radiation used may be harmful to one's health.[45] Fewer than 1% of imaging tests identify the cause of the problem.[9] Imaging may also detect harmless abnormalities, encouraging people to request further unnecessary testing or to worry.[9] Even so, MRI scans of the lumbar region increased by more than 300% among United States Medicare beneficiaries from 1994 to 2006.[11]

In the majority of cases, a hip sprain begins as a microscopic tear that gradually increases in size with repetitive use of the hip. These types of tears are common in sports like cycling, running, swimming, baseball, and golf due to overuse of the hip. If diagnosed early, Grade I and Grade II strains can be effectively treated with rest and other conservative treatments. Grade III strains, however, are one of the most serious hip injuries. This is especially true if the strain is accompanied by a fracture. If your hip cannot bear weight, it is imperative that you contact an orthopaedist for professional treatment.
Traction involves the use of weights and pulleys to apply constant or intermittent force to gradually “pull” the skeletal structure into better alignment. Some people experience pain relief while in traction, but that relief is usually temporary. Once traction is released the back pain tends to return. There is no evidence that traction provides any longterm benefits for people with low back pain.
Stretching the hip muscles that sit on top of the bursae, part of the lining in your hip joint, can give you some relief from bursitis pain. Kneel on the leg that's giving you the pain, holding on to something sturdy for balance. Tilt your pelvis forward, tightening your gluteus muscles (the muscles in your buttocks). Then lean away from the side of your hip that hurts, for instance to the left if you're kneeling on your right knee. You should feel a stretch from the top of your hip bone down the side of your leg to your knee, Humphrey says. Hold the stretch for 30 seconds and repeat once or twice.
Place a mini band around your ankles and spread your feet about shoulder-width apart. Keeping your legs relatively straight (you want the motion to come from your hips) and toes pointing forward, walk forward 10 steps, then backward 10 steps. Take a short break and then walk to the right 10 steps, then to the left 10 steps. Again, focus on keeping your legs straight and toes pointing forward.

Spartacus is worthwhile, but the sex and violence is over-the-top: there’s no sugar-coating it. Definitely not a family drama. But the dramatic quality is excellent. After a couple of campy, awkward episodes at the start, the first season quickly gets quite good: distinctive film craft, interesting writing, and solid acting from nearly the whole cast. Andy Whitfield’s Spartacus is idealistic, earnest, and easy to like. I found it downright upsetting when I learned that he had passed away — as did many, many other fans I’m sure. See my personal blog for a little bit more of a review of Spartacus. BACK TO TEXT
In addition to these exercises, there are simple things you can do every day to help reduce your risk of hip flexor pain. If you sit at a desk for long periods of time, try to get up and move around every hour or so. Warm up properly before any physical activity, and stretch regularly at the end of each workout. Your hips will thank you for it!
Strength training is another key part of the “do” category, Dr. Vasileff says. “It’s a good idea to focus on quad, hamstring, and glute strength,” he says. These muscles surround your hips and provide support, along with your core—which is another area to focus on. “Strengthening your core helps to normalize your walking pattern and stabilize how your pelvis and hips move,” Dr. Vasileff says. That translates to less pain and better hip mobility.

Spondylolisthesis. This condition occurs when one vertebra slips over the adjacent one. There are 5 types of spondylolisthesis but the most common are secondary to a defect or fracture of the pars (between the facet joints) or mechanical instability of the facet joints (degenerative). The pain can be caused by instability (back) or compression of the nerves (leg).
Epidural injections of steroid drugs are frequently used to treat sciatica, despite limited evidence for their effectiveness. Moreover, these treatments are based on the assumption that reducing local inflammation in the vertebral column will relieve pain, but an association between structural abnormalities, inflammation, and sciatica symptoms has not been clearly demonstrated. NINDS-funded researchers are using a new imaging technique that can detect inflammation to better understand what causes chronic sciatica pain and to provide evidence to inform treatment selection. 
Premkumar et al present evidence that the traditional “red flags” for ominous causes of back pain can be quite misleading. The correlation between red flags and ominous diagnoses is poor, and prone to producing false negatives: that is, no red flags even when there is something more serious than unexplained pain going on. In a survey of almost 10,000 patients “the absence of red flag responses did not meaningfully decrease the likelihood of a red flag diagnosis.“ This is not even remotely a surprise to anyone who paid attention in back pain school, but it’s good to have some harder data on it.
Discography may be used when other diagnostic procedures fail to identify the cause of pain. This procedure involves the injection of a contrast dye into a spinal disc thought to be causing low back pain. The fluid’s pressure in the disc will reproduce the person’s symptoms if the disc is the cause. The dye helps to show the damaged areas on CT scans taken following the injection. Discography may provide useful information in cases where people are considering lumbar surgery or when their pain has not responded to conventional treatments.

Behavioral therapy may be useful for chronic pain.[16] There are several types available, including operant conditioning, which uses reinforcement to reduce undesirable behaviors and increase desirable behaviors; cognitive behavioral therapy, which helps people identify and correct negative thinking and behavior; and respondent conditioning, which can modify an individual's physiological response to pain.[17] The benefit however is small.[91] Medical providers may develop an integrated program of behavioral therapies.[17] The evidence is inconclusive as to whether mindfulness-based stress reduction reduces chronic back pain intensity or associated disability, although it suggests that it may be useful in improving the acceptance of existing pain.[92][93]
Foraminotomy is an operation that “cleans out” or enlarges the bony hole (foramen) where a nerve root exits the spinal canal. Bulging discs or joints thickened with age can cause narrowing of the space through which the spinal nerve exits and can press on the nerve, resulting in pain, numbness, and weakness in an arm or leg. Small pieces of bone over the nerve are removed through a small slit, allowing the surgeon to cut away the blockage and relieve pressure on the nerve.

How to do it: Stand with your feet together, holding dumbbells by your sides. Take a wide step out to your right and lower into a side lunge, reaching dumbbells on either side of right leg [as shown]. Bend your left knee and shift your weight into both legs, into a wide squat position, reaching the dumbbells to floor in front of you, then extend your right leg and shift your weight to the left, moving into a side lunge with your left leg.
To ease the pain and lower your odds of an injury, don’t try to do too much at once. “Start with just 10 minutes,” says Arina Garg, MD, a rheumatology fellow at The Center for Excellence for Arthritis and Rheumatology at the Louisiana University Health Sciences Center. “Every few days, increase that time by 5 to 10 minutes.” Your goal is to work up to 30 minutes of aerobic exercise, 5 days a week.

Hip fractures, or a break in the hip bone, are another common cause of hip pain. Fractures of the hip often occur after falls in the elderly patient population. Osteoporosis puts this population at increased risk for hip fractures. Stress fractures are another form of fracture that can cause hip pain. Various risk factors increase one's risk of developing a stress fracture at the hip joint.
Following any period of prolonged inactivity, a regimen of low-impact exercises is advised. Speed walking, swimming, or stationary bike riding 30 minutes daily can increase muscle strength and flexibility. Yoga also can help stretch and strengthen muscles and improve posture. Consult a physician for a list of low-impact, age-appropriate exercises that are specifically targeted to strengthening lower back and abdominal muscles.
Herbal medicines, as a whole, are poorly supported by evidence.[90] The herbal treatments Devil's claw and white willow may reduce the number of individuals reporting high levels of pain; however, for those taking pain relievers, this difference is not significant.[17] Capsicum, in the form of either a gel or a plaster cast, has been found to reduce pain and increase function.[17]
Epidural steroid injections are a commonly used short-term option for treating low back pain and sciatica associated with inflammation. Pain relief associated with the injections, however, tends to be temporary and the injections are not advised for long-term use. An NIH-funded randomized controlled trial assessing the benefit of epidural steroid injections for the treatment of chronic low back pain associated with spinal stenosis showed that long-term outcomes were worse among those people who received the injections compared with those who did not.
The big idea of classification-based cognitive functional therapy (CB-CFT or just CFT) is that most back pain has nothing to do with scary spinal problems and so the cycle of pain and disability can be broken by easing patient fears and anxieties. For this study, CFT was tried with 62 patients and compared to 59 who were treated with manual therapy and exercise. The CFT group did better: a 13-point boost on a 100-point disability scale, and 3 points on a 10-point pain scale. As the authors put it for BodyInMind.org, “Disabling back pain can change for the better with a different narrative and coping strategies.” These results aren’t proof that the confidence cure works, but they are promising.
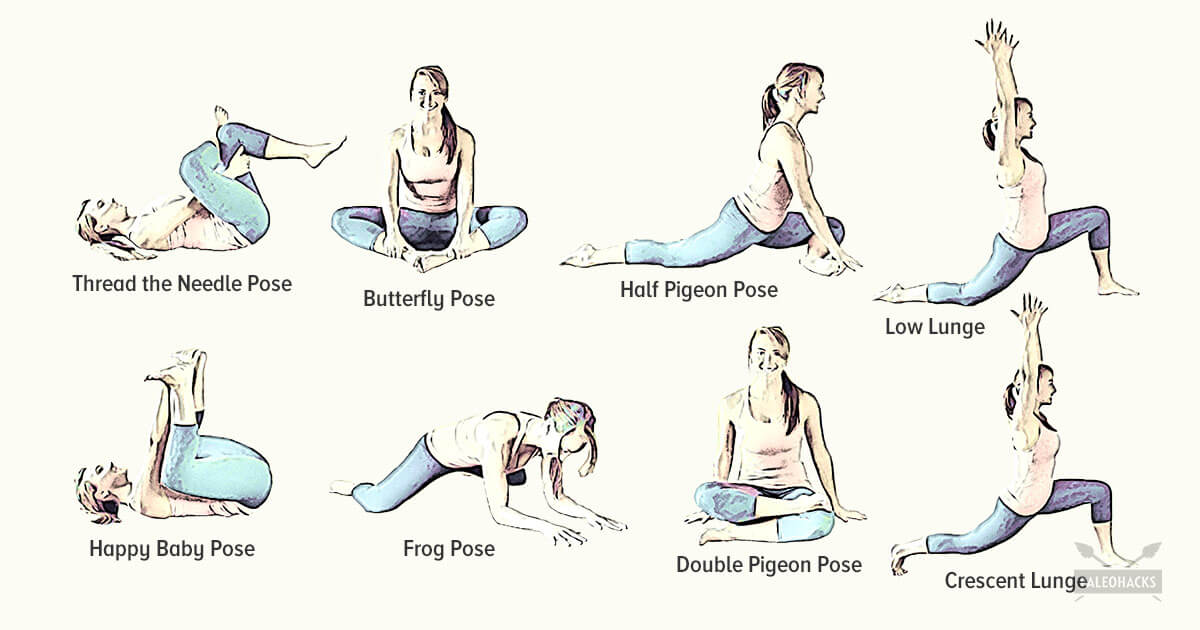
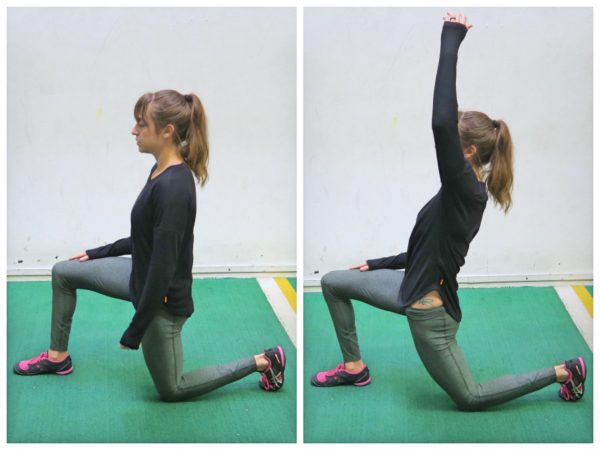
For the 31 million Americans who suffer from daily back pain, relief can be hard to find. In fact, back pain is the single leading cause of disability worldwide and the second most common reason for visits to the doctor. While it can be caused by many different things—extended periods of sitting or standing at work, bad posture, stress, an overly-strenuous workout or helping a friend move, to mention a few—once back pain hits, it can stick around for a long time. Your gut instinct might be to stay frozen until it goes away, but the best thing for your back is to keep it moving with gentle stretches. In fact, a regular routine of a few quick exercises can help you reduce your back pain without a trip to the doctor. Try to do the following exercises every morning and again at night.
There are a few most common causes of hip pain. The first thing to distinguish is to identify which pain is coming from the hip, as opposed to some other source. So there are four causes of hip pain, and the pain can come from muscles, ligaments, tendons, and within the joint itself. But those types of pain present in different ways. So those are the most important distinguishing factors to find out if the hip actually is the cause of the pain.
Doing the bridge exercise in the morning gets your muscles working, activated, and engaged and will help support you the rest of the day, says Humphrey. Lie on your back with your legs bent and your feet flat on the floor, hip-width apart. Press down through your ankles and raise your buttocks off the floor while you tighten your abdominal muscles. Keep your knees aligned with your ankles and aim for a straight line from knees to shoulders, being sure not to arch your back; hold this position for three to five seconds and then slowly lower your buttocks back to the floor. Start with one set of 10 and build up to two or three sets.
When I do a deep knee bend like a sumo squat I get a popping in the outside of my left knee. It feels like a big tendon or ligament is slipping per something. It isn’t painful peer se but I’m afraid if I do it a lot it will be. Is that a relatively common symptom for a guy with tight flexors, it bands, etc? Should I just push through it or have it checked out?
Following any period of prolonged inactivity, a regimen of low-impact exercises is advised. Speed walking, swimming, or stationary bike riding 30 minutes daily can increase muscle strength and flexibility. Yoga also can help stretch and strengthen muscles and improve posture. Consult a physician for a list of low-impact, age-appropriate exercises that are specifically targeted to strengthening lower back and abdominal muscles.

How to: Stand tall, feet slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, toes pointed out at 45-degree angles (a). Keep your back straight, knees over toes and your weight in the heels of your feet (b). Engage your glutes and thighs as you lower into a deep squat until thighs parallel to the ground (or as close as you can get them) (c). Powering through your heels, push up to return to starting position (d). Repeat.

Great exercises and stretches that can be easily done throughout the day to strengthen and loosen my hip flexors. i have very tight hip flexors so it's very helpful for me knowing these exercises and stretches. For those that want more info about exercises and stretches for hip flexors, i recommend the "unlock your hip flexors". It is a program that will show you many more exercises and stretches you can do. So check it out here
How to: Position yourself on your hands and knees, in tabletop position. Engage your abs engaged by pulling your belly button in towards your spine (a). Keeping your hips pointed towards the ground and leg bent to a 90-degree angle, raise your left knee out to the side as high as you can (b). Pause at the top, then return to starting position (c). Repeat, then switch legs.
For example, your quadriceps muscles are a group of four that are located at the front of the thigh; one of the group members, the rectus femoris flexes the hip, which brings your lower extremity (thigh, lower leg, and foot) forward, in front of you. On the other hand, your hamstring muscles are located at the back of the thigh. When they contract, they extend the lower extremity, bringing it behind you.


