To help you strengthen these important muscles, Miranda put together a list of exercises, below. They include dynamic warm-up moves, meant to activate your hip muscles and prep them for the bigger movements to come; functional moves that train basic movement patterns, like the squat, hip hinge, and lunge; functional plyometric exercises that train explosive power; and a few moves that get you moving in different planes of motion, or directions.
Muscle Imbalances – The front of your hips, your hip flexors, are the muscles that will tighten and shorten while you are sitting for hours each day. While you are sitting, the back of your hips, your glutes and your hip extensors, are being overstretched. But just because they are being tightened and stretched respectively, doesn’t benefit either of them. They are also being weakened because of the lack of use of each muscle group.
The lumbar (or lower back) region is made up of five vertebrae (L1–L5), sometimes including the sacrum. In between these vertebrae are fibrocartilaginous discs, which act as cushions, preventing the vertebrae from rubbing together while at the same time protecting the spinal cord. Nerves come from and go to the spinal cord through specific openings between the vertebrae, providing the skin with sensations and messages to muscles. Stability of the spine is provided by the ligaments and muscles of the back and abdomen. Small joints called facet joints limit and direct the motion of the spine.[30]
If surgery is recommended, neurosurgeons have a variety of options available to help relieve pressure on the nerve roots. If there are several nerve roots and discs causing the pain or if there is degeneration and instability in the spinal column, the neurosurgeon may opt to fuse the vertebrae together with bone grafts and stabilize the vertebrae with instrumentation, including metal plates, screws, rods and cages. A successful fusion will prevent the disc from bulging or herniating again. Following a fusion procedure, a patient may gain restored mobility in the back, including the ability to bend over. He or she will most likely experience more mobility after surgery than before. In addition, the patient may require postoperative physical therapy.
Our Keep-It™ guarantee is valid for the first-time purchase of a formula, and redeemable up to three months (90 days) after the purchase date. Multiple bottles, foods, apparel and gear do not fall under this guarantee, however, they may be applicable for return. Fitness equipment, personal care products, knowledge purchases, and DVDs are not eligible for return or refund. For more information and a full list of products that qualify, visit our Keep-It™ page. Further details can be found on our Refund Policy support page.
Why is back pain still a huge problem? Maybe this: “It is extremely difficult to alter the potentially disabling belief among the lay public that low back pain has a structural mechanical cause. An important reason for this is that this belief continues to be regularly reinforced by the conditions of care of a range of ‘hands-on’ providers, for whom idiosyncratic variations of that view are fundamental to their professional existence.”

© 2019 Condé Nast. All rights reserved. Use of and/or registration on any portion of this site constitutes acceptance of our User Agreement (updated 5/25/18) and Privacy Policy and Cookie Statement (updated 5/25/18). SELF may earn a portion of sales from products that are purchased through our site as part of our Affiliate Partnerships with retailers. Your California Privacy Rights. SELF does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Any information published on this website or by this brand is not intended as a substitute for medical advice, and you should not take any action before consulting with a healthcare professional. The material on this site may not be reproduced, distributed, transmitted, cached or otherwise used, except with the prior written permission of Condé Nast. Ad Choices
A sedentary lifestyle can lead to having weak and tight hip flexors as they are always in the shortened position. Tight hip flexors can lead to a limited range of motion, poor posture, lower back, and hip pain, and even injuries. These muscles need to get a workout when you are standing and doing movements such as raising your leg to climb stairs, run, or ride a bicycle.
Melissa Conrad Stöppler, MD, is a U.S. board-certified Anatomic Pathologist with subspecialty training in the fields of Experimental and Molecular Pathology. Dr. Stöppler's educational background includes a BA with Highest Distinction from the University of Virginia and an MD from the University of North Carolina. She completed residency training in Anatomic Pathology at Georgetown University followed by subspecialty fellowship training in molecular diagnostics and experimental pathology.
Initial management with non–medication based treatments is recommended.[6] NSAIDs are recommended if these are not sufficiently effective.[6] Normal activity should be continued as much as the pain allows.[2] Medications are recommended for the duration that they are helpful.[13] A number of other options are available for those who do not improve with usual treatment. Opioids may be useful if simple pain medications are not enough, but they are not generally recommended due to side effects.[4][13] Surgery may be beneficial for those with disc-related chronic pain and disability or spinal stenosis.[14][15] No clear benefit has been found for other cases of non-specific low back pain.[14] Low back pain often affects mood, which may be improved by counseling or antidepressants.[13][16] Additionally, there are many alternative medicine therapies, including the Alexander technique and herbal remedies, but there is not enough evidence to recommend them confidently.[17] The evidence for chiropractic care[18] and spinal manipulation is mixed.[17][19][20][21]

The hip joint is designed to withstand a fair amount of wear and tear, but it’s not indestructible. For example, when you walk, a cushion of cartilage helps prevent friction as the hip bone moves in its socket. With age and use, this cartilage can wear down or become damaged, or the hip bone itself can be fractured during a fall. In fact, more than 300,000 adults over 65 are hospitalized for hip fractures each year, according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.

Enthoven WT, Geuze J, Scheele J, et al. Prevalence and "Red Flags" Regarding Specified Causes of Back Pain in Older Adults Presenting in General Practice. Phys Ther. 2016 Mar;96(3):305–12. PubMed #26183589. How many cases of back pain in older adults have a serious underlying cause? Only about 6% … but 5% of those are fractures (which are serious, but they aren’t cancer either). The 1% is divided amongst all other serious causes. In this study of 669 patients, a vertebral fracture was found in 33 of them, and the chances of this diagnosis was higher in older patients with more intense pain in the upper back, and (duh) trauma. BACK TO TEXT
Take a step back and think about where you spend most of your day. If you're a young athlete, you probably spend most of your time at school or maybe work or practice and even a little time at home, if you're lucky. Now think about what position your body is in during those periods. I would bet that you spend most of your day sitting down. You may walk to class or run in practice, but the majority of your day is spent in a seated position.
Spartacus is worthwhile, but the sex and violence is over-the-top: there’s no sugar-coating it. Definitely not a family drama. But the dramatic quality is excellent. After a couple of campy, awkward episodes at the start, the first season quickly gets quite good: distinctive film craft, interesting writing, and solid acting from nearly the whole cast. Andy Whitfield’s Spartacus is idealistic, earnest, and easy to like. I found it downright upsetting when I learned that he had passed away — as did many, many other fans I’m sure. See my personal blog for a little bit more of a review of Spartacus. BACK TO TEXT

This Australian study concluded that “prognosis is moderately optimistic for patients with chronic low back pain,” contradicting the common fear that any low back pain that lasts longer than 6-9 weeks will become a long-term chronic problem. This evidence is the first of its kind, a rarity in low back pain research, a field where almost everything has been studied to death. “Many studies provide good evidence for the prognosis of acute low back pain,” the authors explain. “Relatively few provide good evidence for the prognosis of chronic low back pain.”
Avoiding injury to the low back is a method of preventing low back pain. Additionally, conditioning exercise programs designed to strengthen the lumbar area and adjacent tissues can help to minimize risk of injury to the low back. Specific programs to relieve and prevent back pain can be designed with the help of physical therapists and other treating health-care professionals.
For persistent low back pain, the short-term outcome is also positive, with improvement in the first six weeks but very little improvement after that. At one year, those with chronic low back pain usually continue to have moderate pain and disability.[2] People at higher risk of long-term disability include those with poor coping skills or with fear of activity (2.5 times more likely to have poor outcomes at one year),[96] those with a poor ability to cope with pain, functional impairments, poor general health, or a significant psychiatric or psychological component to the pain (Waddell's signs).[96]
Stand tall with your hips square and bend your right knee, bringing your foot towards your bum. Grab the right foot with your right hand and actively pull the foot closer to your glutes. As you do this, send the right knee down towards the ground and keep both knees together. squeeze your butt to promote a posterior pelvic tilt and hold — then switch sides.

There are many causes of hip joint pain. Some hip pain is temporary, while other hip pain can be long-standing or chronic. Causes of hip pain include arthritis, inflammatory and noninflammatory arthritis, fracture, sprain, infectious arthritis (septic arthritis), avascular necrosis, Gaucher's disease, sciatica, muscle strain, iliotibial band syndrome (IT band syndrome), and hematoma.
Why is back pain still a huge problem? Maybe this: “It is extremely difficult to alter the potentially disabling belief among the lay public that low back pain has a structural mechanical cause. An important reason for this is that this belief continues to be regularly reinforced by the conditions of care of a range of ‘hands-on’ providers, for whom idiosyncratic variations of that view are fundamental to their professional existence.”
Radicular pain. This type of pain can occur if a spinal nerve root becomes impinged or inflamed. Radicular pain may follow a nerve root pattern or dermatome down into the buttock and/or leg. Its specific sensation is sharp, electric, burning-type pain and can be associated with numbness or weakness (sciatica). It is typically felt on only one side of the body.

The discs are pads that serve as "cushions" between the individual vertebral bodies. They help to minimize the impact of stress forces on the spinal column. Each disc is designed like a jelly donut with a central, softer component (nucleus pulposus) and a surrounding, firm outer ring (annulus fibrosus). The central portion of the disc is capable of rupturing (herniating as in a herniated disc) through the outer ring, causing irritation of adjacent nervous tissue and sciatica as described below. Ligaments are strong fibrous soft tissues that firmly attach bones to bones. Ligaments attach each of the vertebrae to each other and surround each of the discs.
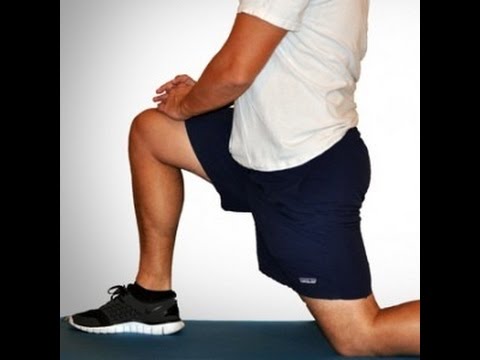
Stretching the hip muscles that sit on top of the bursae, part of the lining in your hip joint, can give you some relief from bursitis pain. Kneel on the leg that's giving you the pain, holding on to something sturdy for balance. Tilt your pelvis forward, tightening your gluteus muscles (the muscles in your buttocks). Then lean away from the side of your hip that hurts, for instance to the left if you're kneeling on your right knee. You should feel a stretch from the top of your hip bone down the side of your leg to your knee, Humphrey says. Hold the stretch for 30 seconds and repeat once or twice.


