^ Jump up to: a b c d e f Qaseem, A; Wilt, TJ; McLean, RM; Forciea, MA; Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of, Physicians. (4 April 2017). "Noninvasive Treatments for Acute, Subacute, and Chronic Low Back Pain: A Clinical Practice Guideline From the American College of Physicians". Annals of Internal Medicine. 166 (7): 514–530. doi:10.7326/M16-2367. PMID 28192789.
Chronic back pain is defined as pain that persists for 12 weeks or longer, even after an initial injury or underlying cause of acute low back pain has been treated. About 20 percent of people affected by acute low back pain develop chronic low back pain with persistent symptoms at one year. In some cases, treatment successfully relieves chronic low back pain, but in other cases pain persists despite medical and surgical treatment.
A complete medical history and physical exam can usually identify any serious conditions that may be causing the pain. During the exam, a health care provider will ask about the onset, site, and severity of the pain; duration of symptoms and any limitations in movement; and history of previous episodes or any health conditions that might be related to the pain. Along with a thorough back examination, neurologic tests are conducted to determine the cause of pain and appropriate treatment. The cause of chronic lower back pain is often difficult to determine even after a thorough examination.
Physician specialties that evaluate and treat low back pain range from generalists to subspecialists.These specialties include emergency medicine physicians, general medicine, family medicine, internal medicine, gynecology, spine surgeons (orthopaedics and neurosurgery), rheumatology, pain management, and physiatry. Other health care providers for low back pain include physical therapists, chiropractors, massage therapists, psychologists, and acupuncturists. 
Doing the bridge exercise in the morning gets your muscles working, activated, and engaged and will help support you the rest of the day, says Humphrey. Lie on your back with your legs bent and your feet flat on the floor, hip-width apart. Press down through your ankles and raise your buttocks off the floor while you tighten your abdominal muscles. Keep your knees aligned with your ankles and aim for a straight line from knees to shoulders, being sure not to arch your back; hold this position for three to five seconds and then slowly lower your buttocks back to the floor. Start with one set of 10 and build up to two or three sets.
Congenital bone conditions: Congenital causes (existing from birth) of low back pain include scoliosis and spina bifida. Scoliosis is a sideways (lateral) curvature of the spine that can be caused when one lower extremity is shorter than the other (functional scoliosis) or because of an abnormal architecture of the spine (structural scoliosis). Children who are significantly affected by structural scoliosis may require treatment with bracing and/or surgery to the spine. Adults infrequently are treated surgically but often benefit by support bracing. Spina bifida is a birth defect in the bony vertebral arch over the spinal canal, often with absence of the spinous process. This birth defect most commonly affects the lowest lumbar vertebra and the top of the sacrum. Occasionally, there are abnormal tufts of hair on the skin of the involved area. Spina bifida can be a minor bony abnormality without symptoms. However, the condition can also be accompanied by serious nervous abnormalities of the lower extremities.

Why is back pain still a huge problem? Maybe this: “It is extremely difficult to alter the potentially disabling belief among the lay public that low back pain has a structural mechanical cause. An important reason for this is that this belief continues to be regularly reinforced by the conditions of care of a range of ‘hands-on’ providers, for whom idiosyncratic variations of that view are fundamental to their professional existence.”
Approximately 9–12% of people (632 million) have LBP at any given point in time, and nearly 25% report having it at some point over any one-month period.[7][8] About 40% of people have LBP at some point in their lives,[7] with estimates as high as 80% among people in the developed world.[22] Difficulty most often begins between 20 and 40 years of age.[1] Men and women are equally affected.[4] Low back pain is more common among people aged between 40 and 80 years, with the overall number of individuals affected expected to increase as the population ages.[7]
Strong muscles support and protect your joints. “Strengthening the lower body takes some of the pressure off of the hip and knee joints,” says William Oswald, DPT, a physical therapist and clinical instructor of rehabilitation medicine at NYU Langone Health. This can relieve some of the pain and protect against more damage. “It can also make daily tasks, such as climbing the stairs, easier,” he says.
"Lower back pain is the most common musculoskeletal ailment in the U.S., and can often be mitigated by strengthening the core musculature," Blake Dircksen, D.P.T., C.S.C.S., a physical therapist at Bespoke Treatments New York, tells SELF. "The 'core' is a cylinder of abdominal and back muscles that wraps around the body like a corset," Dircksen explains. (The glutes are also considered a part of the core, since they connect to the pelvis and ultimately the back and abdominal muscles.) As with any muscles, by strengthening them, you will increase the amount of weight your lower back can comfortably move, which means it will be better equipped to handle the same stress from your workouts and everyday life without getting as achey.
The only activity performed on a regular basis that fully extends the hip is walking and running. Hence as activity levels decrease so does the ability to extend the hip. This results in compensatory pelvic tilting and lumbar extension, with a reduction in the ability to accommodate uneven ground, negotiate obstacles, or attempt to change walking speed quickly. The compensatory pelvic tilt that accompanies tight hip flexors also predisposes the individual to postural problems and back pain. Hip stretches done on a regular basis can help you maintain extension range of motion and thereby improve function.
One of the biggest dangers to your health is constantly sitting for long periods of time which can cause physical and emotional damage. 10 key moves that will help loosen your hip flexor and unlock the power within your body. There is an easy to follow program to unlocking your hip flexors that will strengthen your body, improve your health, and have an all day energy..... https://bit.ly/2HYTPrJ Report
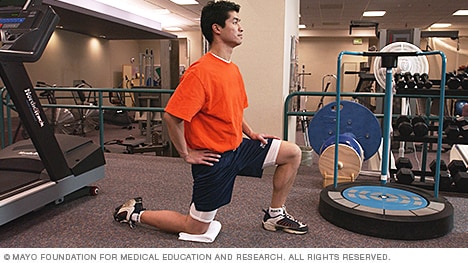
Kneel with a wall or pillar behind you, knees hips-width apart and toes touching the wall. Arch your back to lean back while keeping your hips stacked over your knees. Take your arms overhead and touch your palms into the wall behind you. This bend does not need to be extremely deep to feel a great stretch in the hips and strength in the lower back.

The side of the pain on its own doesn’t tell us much, and most of the one-sided sources of pain are viscera that usually cause abdominal pain instead of back pain, or in addition to it. In other words, the only reason to worry about right or left lower back pain is if it is otherwise worrisome: if you have other red flags or significant non-back symptoms.
Pain in the hip can result from a number of factors. Sometimes diseases that affect other joints in the body, such as the inflammation resulting from arthritis, can be the cause of pain in the hip. Depending upon the cause of hip pain, the pain may occur when walking, running, or engaging in activity. Trochanteric bursitis is the most common type of hip bursitis and causes pain at the point of the hip.

Lumbar herniated disc. The jelly-like center of a lumbar disc can break through the tough outer layer and irritate a nearby nerve root. The herniated portion of the disc is full of proteins that cause inflammation when they reach a nerve root, and inflammation as well as nerve compression cause nerve root pain. The disc wall is also richly supplied by nerve fibers, and a tear through the wall can cause severe pain.
There are a number of ways to classify low back pain with no consensus that any one method is best.[5] There are three general types of low back pain by cause: mechanical back pain (including nonspecific musculoskeletal strains, herniated discs, compressed nerve roots, degenerative discs or joint disease, and broken vertebra), non-mechanical back pain (tumors, inflammatory conditions such as spondyloarthritis, and infections), and referred pain from internal organs (gallbladder disease, kidney stones, kidney infections, and aortic aneurysm, among others).[5] Mechanical or musculoskeletal problems underlie most cases (around 90% or more),[5][34] and of those, most (around 75%) do not have a specific cause identified, but are thought to be due to muscle strain or injury to ligaments.[5][34] Rarely, complaints of low back pain result from systemic or psychological problems, such as fibromyalgia and somatoform disorders.[34]
How to: Get into a high plank position on the floor, hands planted under your shoulders, butt down (a). Engage your abs by pulling your belly button in towards your spine (b). Squeeze your left glute to lift your left leg two inches off the ground, keeping your leg straight (c). Tap your left leg out to the side, then back to starting position. Repeat, then switch legs (d).
If you have hip pain, you may benefit from the skilled services of a physical therapist to help determine the cause of your pain. Your PT can work with you to develop a treatment strategy to treat your hip pain or hip discomfort. Understanding why your hip is hurting can help your physical therapist and doctor prescribe the right treatment regimen for your specific condition.

How to: Sit down with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor in front of you (a). Place your right ankle on top of your left thigh and flex your right foot (b). Put your hands behind your body, fingertips facing away from your body and begin to press your hips toward your heels until you feel a stretch through your outer left hip. Keep your back tall and chest open (c). Hold for six to eight breaths, then repeat on the other side.
If you have a stiff, tight or painful hip then www.HipFlexor.org will unlock your hip flexors and restore movement the way it should be. Unlocking your hip flexors instantly breathes new life, energy, and strength into your body! I experienced immediate results. I've been able to loosen up my hips, decrease back tightness, and even workout harder. With so many people suffering with hip pain out there, this program is a great tool for anybody that wants to reduce pain while improving strength, performance, and overall health. Hip flexibility, mobility and strength is one of the most important things you can do to keep your overall body healthy. The video presentation and visuals in the exercise program give me confidence that I am doing the exercises correctly which for me is key with no personal trainer. The website is very complete in listing the possible causes of tight hip flexors and other factors that can lead to the issue. It has detailed, descriptive information regarding the anatomy of the hip, causes of such injuries, and a very progressive and well-explained exercise and stretching schedule that will assist to re-balance the hip and pelvic region, safely stretch and strengthen the muscle group. Best of luck to you! :) Report
Back pain can suck the joy out of your days for week, months, even years. It can definitely be “serious” even when it’s not dangerous. I have worked with many truly miserable chronic low back pain patients, and of course the huge economic costs of back pain are cited practically anywhere the subject comes up. But your typical case of chronic low back pain, as nasty as it can be, has never killed anyone.
Pain in the hip can result from a number of factors. Sometimes diseases that affect other joints in the body, such as the inflammation resulting from arthritis, can be the cause of pain in the hip. Depending upon the cause of hip pain, the pain may occur when walking, running, or engaging in activity. Trochanteric bursitis is the most common type of hip bursitis and causes pain at the point of the hip.

For example, your quadriceps muscles are a group of four that are located at the front of the thigh; one of the group members, the rectus femoris flexes the hip, which brings your lower extremity (thigh, lower leg, and foot) forward, in front of you. On the other hand, your hamstring muscles are located at the back of the thigh. When they contract, they extend the lower extremity, bringing it behind you.

Hamstring squeeze. Use the machine that works your hamstrings; you will either lie on your stomach or sit with a pad behind your knee. Push against the pad, moving your knee up toward the ceiling or backward (depending on which position you’re in). “In other words, bend your knees,” Pariser says. But to avoid cramps in your hamstring muscles, don’t bend your knee so much that your heels are too close to your buttocks.
Enthoven WT, Geuze J, Scheele J, et al. Prevalence and "Red Flags" Regarding Specified Causes of Back Pain in Older Adults Presenting in General Practice. Phys Ther. 2016 Mar;96(3):305–12. PubMed #26183589. How many cases of back pain in older adults have a serious underlying cause? Only about 6% … but 5% of those are fractures (which are serious, but they aren’t cancer either). The 1% is divided amongst all other serious causes. In this study of 669 patients, a vertebral fracture was found in 33 of them, and the chances of this diagnosis was higher in older patients with more intense pain in the upper back, and (duh) trauma. BACK TO TEXT
^ Chou R, Loeser JD, Owens DK, Rosenquist RW, Atlas SJ, Baisden J, Carragee EJ, Grabois M, Murphy DR, Resnick DK, Stanos SP, Shaffer WO, Wall EM, American Pain Society Low Back Pain Guideline Panel (2009). "Interventional therapies, surgery, and interdisciplinary rehabilitation for low back pain: An evidence-based clinical practice guideline from the American Pain Society". Spine. 34 (10): 1066–77. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181a1390d. PMID 19363457.
In terms of diagnosing hip pain, typically a patient will expect when they come in to be asked about their symptoms, and it’s very important to find out when did these symptoms start, how long they have been going on, how frequent they are, if they come on in the morning or the evening, do they come on with any certain activity, and if there is something that makes it better or worse. The intensity of the pain is also important. Does it have any associated radiating symptoms? Is it localized in one spot or does it move? After getting a history and finding out what type of pain the patient is having, which also includes whether the pain is dull, aching, sharp, or intense, then it’s important to do a good physical exam. The physical examination involves testing the muscle strength, testing for sensation, doing provocative maneuvers which might help us rule out one type of injury from another.

Marvelously progressive, concise, and cogent guidelines for physicians on the treatment of low back pain. These guidelines almost entirely “get it right” in my opinion, and are completely consistent with recommendations I’ve been making for years on PainScience.com. They are particularly to be praised for strongly discouraging physicians from ordering imaging tests only “for patients with low back pain when severe or progressive neurologic deficits are present or when serious underlying conditions are suspected.”
Several NIH-funded clinical trials and other studies in patients aim to improve treatment options and prevention strategies for chronic low back pain, as well as add to the evidence base about existing treatments. A multi-year multicenter study called the Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial (SPORT) compared the most commonly used surgical and nonsurgical treatments for patients with the three most common diagnoses for which spine surgery is performed: intervertebral disc herniation, spinal stenosis, and degenerative spondylisthesis. SPORT represented the largest clinical investigation to date looking at treatment results for these disabling and costly causes of chronic low back pain.
References to any non-Onnit entity, product, service, person or source of information in this or any other Communication should not be considered an endorsement, either direct or implied, by the host, presenter or distributor of the Communication. The host(s), presenter(s) and/or distributor(s) of this Communication are not responsible for the content of any non-Onnit internet pages referenced in the Communication. Onnit is not liable or responsible for any advice, course of treatment, diagnosis or any other information or services you chose to follow without consulting a qualified medical professional. Before starting any new diet and/or exercise program, always be sure to check with your qualified medical professional.
Exercise therapy is effective in decreasing pain and improving function for those with chronic low back pain.[50] It also appears to reduce recurrence rates for as long as six months after the completion of program[61] and improves long-term function.[57] There is no evidence that one particular type of exercise therapy is more effective than another.[62] The Alexander technique appears useful for chronic back pain,[63] and there is tentative evidence to support the use of yoga.[64] Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) has not been found to be effective in chronic low back pain.[65] Evidence for the use of shoe insoles as a treatment is inconclusive.[51] Peripheral nerve stimulation, a minimally-invasive procedure, may be useful in cases of chronic low back pain that do not respond to other measures, although the evidence supporting it is not conclusive, and it is not effective for pain that radiates into the leg.[66]

Back pain can suck the joy out of your days for week, months, even years. It can definitely be “serious” even when it’s not dangerous. I have worked with many truly miserable chronic low back pain patients, and of course the huge economic costs of back pain are cited practically anywhere the subject comes up. But your typical case of chronic low back pain, as nasty as it can be, has never killed anyone.

References to any non-Onnit entity, product, service, person or source of information in this or any other Communication should not be considered an endorsement, either direct or implied, by the host, presenter or distributor of the Communication. The host(s), presenter(s) and/or distributor(s) of this Communication are not responsible for the content of any non-Onnit internet pages referenced in the Communication. Onnit is not liable or responsible for any advice, course of treatment, diagnosis or any other information or services you chose to follow without consulting a qualified medical professional. Before starting any new diet and/or exercise program, always be sure to check with your qualified medical professional.

Multiple sclerosis (MS) symptoms vary from person to person, and can last for days to months without periods of remission. Symptoms of MS include sexual problems and problems with the bowel, bladder, eyes, muscles, speech, swallowing, brain, and nervous system. The early symptoms and signs of multiple sclerosis usually start between age 20 and 40. MS in children, teens, and those over age 40 is rare. Treatment options for multiple sclerosis vary depending on the type and severity of symptoms. Medications may be prescribed to manage MS symptoms.
Like quadriceps, the hamstrings are 2-joint muscles. Unlike the quadriceps, though, the hamstrings reside at the back of your thigh. They attach at the siting bones, which are located on the underside of your pelvis. When the hamstring muscles contract, the effect is a pulling of the back of the pelvis down toward the back of the thigh, or a bringing of the lower extremity back behind you.
This information is not designed to replace a physician's independent judgment about the appropriateness or risks of a procedure for a given patient. Always consult your doctor about your medical conditions or back problem. SpineUniverse does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Use of the SpineUniverse.com site is conditional upon your acceptance of our User Agreement

The hip joint is designed to withstand a fair amount of wear and tear, but it’s not indestructible. For example, when you walk, a cushion of cartilage helps prevent friction as the hip bone moves in its socket. With age and use, this cartilage can wear down or become damaged, or the hip bone itself can be fractured during a fall. In fact, more than 300,000 adults over 65 are hospitalized for hip fractures each year, according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
Men and women are equally affected by low back pain, which can range in intensity from a dull, constant ache to a sudden, sharp sensation that leaves the person incapacitated. Pain can begin abruptly as a result of an accident or by lifting something heavy, or it can develop over time due to age-related changes of the spine. Sedentary lifestyles also can set the stage for low back pain, especially when a weekday routine of getting too little exercise is punctuated by strenuous weekend workout.
Like quadriceps, the hamstrings are 2-joint muscles. Unlike the quadriceps, though, the hamstrings reside at the back of your thigh. They attach at the siting bones, which are located on the underside of your pelvis. When the hamstring muscles contract, the effect is a pulling of the back of the pelvis down toward the back of the thigh, or a bringing of the lower extremity back behind you.
Physician specialties that evaluate and treat low back pain range from generalists to subspecialists.These specialties include emergency medicine physicians, general medicine, family medicine, internal medicine, gynecology, spine surgeons (orthopaedics and neurosurgery), rheumatology, pain management, and physiatry. Other health care providers for low back pain include physical therapists, chiropractors, massage therapists, psychologists, and acupuncturists.

This Web site provides general educational information on health-related issues and provides access to health-related resources for the convenience of our users. This site and its health-related information and resources are not a substitute for professional medical advice or for the care that patients receive from their physicians or other health care providers.

Strength training is another key part of the “do” category, Dr. Vasileff says. “It’s a good idea to focus on quad, hamstring, and glute strength,” he says. These muscles surround your hips and provide support, along with your core—which is another area to focus on. “Strengthening your core helps to normalize your walking pattern and stabilize how your pelvis and hips move,” Dr. Vasileff says. That translates to less pain and better hip mobility.

Avascular necrosis (also called osteonecrosis). This condition happens when blood flow to the hip bone slows and the bone tissue dies. Although it can affect other bones, avascular necrosis most often happens in the hip. It can be caused by a hip fracture or dislocation, or from the long-term use of high-dose steroids (such as prednisone), among other causes.
Meanwhile, it’s extremely common for non-life-threatening low back pain to be alarmingly severe and persistent — to have a loud bark! Your doctor may not appreciate how true this is, and may over-react to all persistent low back pain, even without other red flags. In most cases, you shouldn’t let them scare you. Being “freaked out” about persistent back pain is the real threat: it can make low back pain much worse, and much more likely to last even longer (a tragic irony).
Endometriosis (when the uterus lining grows somewhere else) can cause pelvic tenderness, which some women describe as hip pain. Pain from the back and spine also can be felt around the buttocks and hip, Siegrist says. Sciatica, a pinched nerve, typically affects one side of the body and can cause pain in the back of the right or left hip — the pain from sciatica can start in your lower back and travel down to your buttocks and legs.

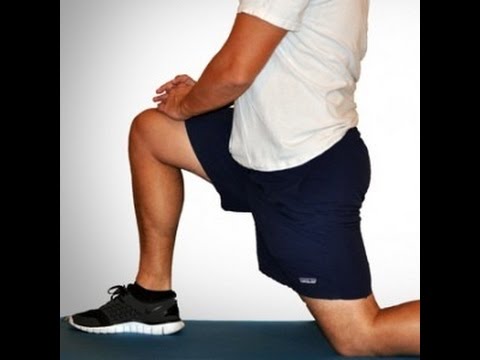
To stretch your quadriceps at the hip, the idea is to do the opposite movement to flexion, i.e., extension. You can perform extension moves at the hip while standing, lying on your side, lying prone (on your stomach) and kneeling. Even basic stretches done at a pain-free level where you can feel a small bit of challenge, and that are held continuously for approximately 30 seconds may translate to better posture and less back pain.
“Red flags” are signs or symptoms that something medically ominous may be going on. Red flags are not reliable, and their presence is not a diagnosis. When you have some red flags, it only indicates a need to look more closely. Sometimes red flags are missing there really is something serious going on … and sometimes they are a false alarm.18 Check off all that apply … hopefully none or few or only the least alarming of them!
This game-changing mat is what every yogi wishes they could practice in. Its smooth top layer provides better grip for tricky poses and sweaty hot yoga sessions. The thick fabric supports knees and elbows when you're in plank and pigeon. But what sets this yoga mat apart is its ability to roll up on its own and snap in place. This self-rolling mat also pairs with the Women's Health Amazon Alexa app, which walks you through the flow of the day.
Just because your hip flexor region feels sore doesn’t necessarily mean the muscles there are tight — in fact, they might need strengthening. This is where that sports science debate we mentioned earlier comes into play. It’s important to identify whether you’re tight or if the muscles are weak. Again, the Thomas Test will help you identify if you’re maybe stretching something that actually needs strengthening.
Keeping your hips mobile is important for overall hip function and athletic performance. Mobility refers to the ability of your joints to move through a pain-free, unrestricted range of motion. For cyclists, hip mobility is critical since pedaling occurs in one plane of motion, and after miles and miles in the saddle, hip tightness and restriction may develop. The following movements will help with hip mobility.
Exercise therapy is effective in decreasing pain and improving function for those with chronic low back pain.[50] It also appears to reduce recurrence rates for as long as six months after the completion of program[61] and improves long-term function.[57] There is no evidence that one particular type of exercise therapy is more effective than another.[62] The Alexander technique appears useful for chronic back pain,[63] and there is tentative evidence to support the use of yoga.[64] Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) has not been found to be effective in chronic low back pain.[65] Evidence for the use of shoe insoles as a treatment is inconclusive.[51] Peripheral nerve stimulation, a minimally-invasive procedure, may be useful in cases of chronic low back pain that do not respond to other measures, although the evidence supporting it is not conclusive, and it is not effective for pain that radiates into the leg.[66]
Degenerative disc disease. At birth, intervertebral discs are full of water and at their healthiest. As people age over time, discs lose hydration and wear down. As the disc loses hydration, it cannot resist forces as well, and transfers force to the disc wall that may develop tears and cause pain or weakening that can lead to a herniation. The disc can also collapse and contribute to stenosis.
The symptoms can also be classified by duration as acute, sub-chronic (also known as sub-acute), or chronic. The specific duration required to meet each of these is not universally agreed upon, but generally pain lasting less than six weeks is classified as acute, pain lasting six to twelve weeks is sub-chronic, and more than twelve weeks is chronic.[3] Management and prognosis may change based on the duration of symptoms.
Intervertebral disc degeneration is one of the most common mechanical causes of low back pain, and it occurs when the usually rubbery discs lose integrity as a normal process of aging. In a healthy back, intervertebral discs provide height and allow bending, flexion, and torsion of the lower back. As the discs deteriorate, they lose their cushioning ability.
Lay on your back on your mat and pull your knees to your chest. Place your hands on the inside arches of your feet and open your knees wider than shoulder-width apart. Keeping your back pressed into the mat as much as possible, press your feet into hands while pulling down on feet, creating resistance. Breathe deeply and hold for at least 30 seconds.
Spinal laminectomy (also known as spinal decompression) is performed when spinal stenosis causes a narrowing of the spinal canal that causes pain, numbness, or weakness. During the procedure, the lamina or bony walls of the vertebrae, along with any bone spurs, are removed. The aim of the procedure is to open up the spinal column to remove pressure on the nerves.

At the start of the 20th century, physicians thought low back pain was caused by inflammation of or damage to the nerves,[99] with neuralgia and neuritis frequently mentioned by them in the medical literature of the time.[100] The popularity of such proposed causes decreased during the 20th century.[100] In the early 20th century, American neurosurgeon Harvey Williams Cushing increased the acceptance of surgical treatments for low back pain.[14] In the 1920s and 1930s, new theories of the cause arose, with physicians proposing a combination of nervous system and psychological disorders such as nerve weakness (neurasthenia) and female hysteria.[99] Muscular rheumatism (now called fibromyalgia) was also cited with increasing frequency.[100]
For the 31 million Americans who suffer from daily back pain, relief can be hard to find. In fact, back pain is the single leading cause of disability worldwide and the second most common reason for visits to the doctor. While it can be caused by many different things—extended periods of sitting or standing at work, bad posture, stress, an overly-strenuous workout or helping a friend move, to mention a few—once back pain hits, it can stick around for a long time. Your gut instinct might be to stay frozen until it goes away, but the best thing for your back is to keep it moving with gentle stretches. In fact, a regular routine of a few quick exercises can help you reduce your back pain without a trip to the doctor. Try to do the following exercises every morning and again at night.
Meanwhile, many non-dangerous problems can cause amazingly severe back pain. A muscle cramp is a good analogy — just think about how painful a Charley horse is! Regardless of what’s actually going on in there, muscle pain is probably the main thing that back pain patients are feeling. The phenomenon of trigger points — tiny muscle cramps, basically11 — could be the entire problem, or a complication that’s more painful and persistent than the original problem. It’s hard to overstate how painful trigger points can be, but they are not dangerous to anything but your comfort.
Analgesic medications are those specifically designed to relieve pain. They include OTC acetaminophen and aspirin, as well as prescription opioids such as codeine, oxycodone, hydrocodone, and morphine. Opioids should be used only for a short period of time and under a physician’s supervision. People can develop a tolerance to opioids and require increasingly higher dosages to achieve the same effect. Opioids can also be addictive. Their side effects can include drowsiness, constipation, decreased reaction time, and impaired judgment. Some specialists are concerned that chronic use of opioids is detrimental to people with back pain because they can aggravate depression, leading to a worsening of the pain.
Really great content. I also had some lower back problem but now that I know the source, I will work on it. My counsins also talked to me about this product called Panifix, or "Unlock your hip flexor" which Gives You A Practical, Easy-to-follow Program You Can Use To Instantly Release Your Hip Flexors For More Strength, Better Health And All Day Energy. Proven Swipes And Creatives Here:https://tinyurl.com/yd6nbzfh
If low back pain occurs after a recent injury — such as a car accident, a fall or sports injury — call your primary-care physician immediately. If there are any neurological symptoms, seek medical care immediately. If there are no neurological problems (i.e. numbness, weakness, bowel and bladder dysfunction), the patient may benefit by beginning conservative treatment at home for two to three days. The patient may take anti-inflammatory medications such as aspirin or ibuprofen and restrict strenuous activities for a few days.


