Our Keep-It™ guarantee is valid for the first-time purchase of a formula, and redeemable up to three months (90 days) after the purchase date. Multiple bottles, foods, apparel and gear do not fall under this guarantee, however, they may be applicable for return. Fitness equipment, personal care products, knowledge purchases, and DVDs are not eligible for return or refund. For more information and a full list of products that qualify, visit our Keep-It™ page. Further details can be found on our Refund Policy support page.
Nerve block therapies aim to relieve chronic pain by blocking nerve conduction from specific areas of the body. Nerve block approaches range from injections of local anesthetics, botulinum toxin, or steroids into affected soft tissues or joints to more complex nerve root blocks and spinal cord stimulation. When extreme pain is involved, low doses of drugs may be administered by catheter directly into the spinal cord. The success of a nerve block approach depends on the ability of a practitioner to locate and inject precisely the correct nerve. Chronic use of steroid injections may lead to increased functional impairment.
Non-mechanical Disease Processes: Sometimes, non-mechanical disease processes like cancer, kidney stones, or a tumor may cause low back pain. These symptoms are usually, but not always, accompanied by other symptoms like unexpected weight loss, fever, or malaise that indicate a non-mechanical cause of your pain. These diseases are rare, but they can happen, so if your back pain continues for more than a few weeks after physical therapy treatment begins, a visit to your doctor is certainly in order to rule out a sinister problem.
When it comes to your workouts, low-impact aerobic exercises are generally best and least likely to cause issues, says Kelton Vasileff, M.D., an orthopedic surgeon at Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center. “I recommend swimming, walking, elliptical, cycling, and stationary biking for general exercise,” he says. All of these are great ways to move your body without pounding your joints.

Lie on your back with your knees bent and your feet flat on the floor. Tighten the muscles in your buttocks, then lift your hips off the ground and hold for about five seconds before slowly lowering yourself back down. Be sure to breathe throughout the exercise. As with the first exercise, you can work up to doing 30 repetitions, resting for a few seconds (or longer) between each. “If you start to get tired, stop and rest for a couple of minutes,” Pariser says.

Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) involves wearing a battery-powered device consisting of electrodes placed on the skin over the painful area that generate electrical impulses designed to block incoming pain signals from the peripheral nerves. The theory is that stimulating the nervous system can modify the perception of pain. Early studies of TENS suggested that it elevated levels of endorphins, the body’s natural pain-numbing chemicals. More recent studies, however, have produced mixed results on its effectiveness for providing relief from low back pain.
Low back pain can be caused by tumors, either benign or malignant, that originate in the bone of the spine or pelvis and spinal cord (primary tumors) and those which originate elsewhere and spread to these areas (metastatic tumors). Symptoms range from localized pain to radiating severe pain and loss of nerve and muscle function (even incontinence of urine and stool) depending on whether or not the tumors affect the nervous tissue. Tumors of these areas are detected using imaging tests, such as plain X-rays, nuclear bone scanning, and CAT and MRI scanning.
When was the last time you got on your gym's abductor or adductor machine and got in a good workout? It's probably been a while. Both are machines that don't get a lot of use, and they are often the target of coaches' ridicule on those "useless gym moves we should all skip" lists. Perhaps rightly so, especially if you're hopping on those machines hoping for a slimming effect.
Apply the above concept to your hips. When you sit, your hips are in a "flexed" position. Therefore, the muscles that flex your hips are in a shortened state. You probably spend at least a third of your day sitting down. Think about how much time those hip flexor muscles stay shortened. A lot. Over time, they become tighter and tighter until you look like the old man in the picture. So unless you want to look like that, perform the stretches shown below.
Degenerative disc disease. At birth, intervertebral discs are full of water and at their healthiest. As people age over time, discs lose hydration and wear down. As the disc loses hydration, it cannot resist forces as well, and transfers force to the disc wall that may develop tears and cause pain or weakening that can lead to a herniation. The disc can also collapse and contribute to stenosis.
Disc degeneration remains a key cause of chronic low back pain and the pain often persists despite surgery. NIH-funded basic science and preclinical studies are investigating molecular-level mechanisms that cause discs in the spine to degenerate, as well as protective mechanisms involved in disc remodeling that may diminish with advancing age. Such studies may help identify future therapeutic strategies to block degenerative mechanisms or promote remodeling processes. NIH also is funding early research on stem cell approaches to promote disc regeneration and rejuvenate cells of the nucleus pulposus, the jelly-like substance in the center of intervertebral discs that loses water content as people age.
The diagnosis of low back pain involves a review of the history of the illness and underlying medical conditions as well as a physical examination. It is essential that a complete story of the back pain be reviewed including injury history, aggravating and alleviating conditions, associated symptoms (fever, numbness, tingling, incontinence, etc.), as well as the duration and progression of symptoms. Aside from routine abdomen and extremity evaluations, rectal and pelvic examinations may eventually be required as well. Further tests for diagnosis of low back pain can be required including blood and urine tests, plain film X-ray tests, CAT scanning, MRI scanning, bone scanning, and tests of the nerves such as electromyograms (EMG) and nerve conduction velocities (NCV).
If you work at a desk job all day, you might have some areas of your workstation to thank for your back pain. Evaluating your space to make it more ergonomic (back-friendly), can help you experience lower back pain relief and prevent pain from getting worse. Rethinking your workspace for back relief starts with positioning your most important work tools.
For those with pain localized to the lower back due to disc degeneration, fair evidence supports spinal fusion as equal to intensive physical therapy and slightly better than low-intensity nonsurgical measures.[15] Fusion may be considered for those with low back pain from acquired displaced vertebra that does not improve with conservative treatment,[14] although only a few of those who have spinal fusion experience good results.[15] There are a number of different surgical procedures to achieve fusion, with no clear evidence of one being better than the others.[83] Adding spinal implant devices during fusion increases the risks but provides no added improvement in pain or function.[11]

Even though low back pain can sometimes be treated without major disruption to a person's life, athletes are often reluctant to seek medical help. Many of them deny or minimize complaints in order to avoid consequences, such as: having to decrease activity in order to recover, losing a position or being removed from a team, missing a competition, or letting the team down. Some athletes simply do not want to bother seeing a doctor for pain; they hope it will recover on its own.
Health Tools Baby Due Date CalculatorBasal Metabolic Rate CalculatorBody Mass Index (BMI) CalculatorCalories Burned CalculatorChild Energy Requirements CalculatorDaily Calcium Requirements CalculatorDaily Fibre Requirements CalculatorIdeal Weight CalculatorInfectious Diseases Exclusion Periods ToolOvulation CalculatorSmoking Cost CalculatorTarget Heart Rate CalculatorWaist-to-hip Ratio Calculator Risk Tests Depression Self-AssessmentErectile Dysfunction ToolMacular Degeneration ToolOsteoporosis Risk TestProstate Symptoms Self-Assessment
Low back pain has been with humans since at least the Bronze Age. The oldest known surgical treatise – the Edwin Smith Papyrus, dating to about 1500 BCE – describes a diagnostic test and treatment for a vertebral sprain. Hippocrates (c. 460 BCE – c. 370 BCE) was the first to use a term for sciatic pain and low back pain; Galen (active mid to late second century CE) described the concept in some detail. Physicians through the end of the first millennium did not attempt back surgery and recommended watchful waiting. Through the Medieval period, folk medicine practitioners provided treatments for back pain based on the belief that it was caused by spirits.[99]

The treatment of lumbar strain consists of resting the back (to avoid reinjury), medications to relieve pain and muscle spasm, local heat applications, massage, and eventual (after the acute episode resolves) reconditioning exercises to strengthen the low back and abdominal muscles. Initial treatment at home might include heat application, acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), and avoiding reinjury and heavy lifting. Prescription medications that are sometimes used for acute low back pain include anti-inflammatory medications, such as sulindac (Clinoril), naproxen (Naprosyn), and ketorolac (Toradol) by injection or by mouth, muscle relaxants, such as carisoprodol (Soma), cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril), methocarbamol (Robaxin), and metaxalone (Skelaxin), as well as analgesics, such as tramadol (Ultram).

I had physical therapy last year for lower back pain and these exercises were part of the regimen. I went 2 to 3 times a week and it actually worked, I was pain free. The therapist stated that as long as I incorporated these exercises into my daily life a few times a week, I would remain pain free. I did just that for a few months and she was right, I felt great. Unfortunately, I took being pain free for a few months for being “cured”, not so, pain is back, which is why I’m online looking for relief. After looking at this website, I realize, I already know what will work, these exercises duh, lol. As soon as I log off, I will hit the mat and as long as these exercises work as well as last year I am determined to do them on a regular basis (like the therapist suggested) and live pain free…at least in my back! 🙂
But moving is important for hip and knee OA. It causes your joints to compress and release, bringing blood flow, nutrients, and oxygen into the cartilage. “This can help prolong the function and longevity of your joints,” says Eric Robertson, DPT, a physical therapist and associate professor of clinical physical therapy at the University of Southern California.

The condition is cauda equina syndrome. It involves “acute loss of function of the neurologic elements (nerve roots) of the spinal canal below the termination (conus) of the spinal cord,” where the nerves spread out like a horse (equina) tail. Again, this condition causes symptoms in the “saddle” of the body: butt, groin, inner thighs. BACK TO TEXT
Place a mini band around your ankles and spread your feet about shoulder-width apart. Keeping your legs relatively straight (you want the motion to come from your hips) and toes pointing forward, walk forward 10 steps, then backward 10 steps. Take a short break and then walk to the right 10 steps, then to the left 10 steps. Again, focus on keeping your legs straight and toes pointing forward.
How to: Get into a high plank position on the floor, hands planted under your shoulders, butt down (a). Engage your abs by pulling your belly button in towards your spine (b). Squeeze your left glute to lift your left leg two inches off the ground, keeping your leg straight (c). Tap your left leg out to the side, then back to starting position. Repeat, then switch legs (d).
The problem is that these muscles aren't designed to be prime movers—they're designed to support the action of the glutes. Inability of activating the glutes can result in low back pain (low back muscles compensating), hamstring strains (overacting hamstrings), hip pain (resulting from hamstring-dominant hip extension) and knee pain (poor glute medius strength).
The materials and information provided in this presentation, document and/or any other communication (“Communication”) from Onnit Labs, Inc. or any related entity or person (collectively “Onnit”) are strictly for informational purposes only and are not intended for use as diagnosis, prevention or treatment of a health problem or as a substitute for consulting a qualified medical professional. Some of the concepts presented herein may be theoretical.
Hamstring squeeze. Use the machine that works your hamstrings; you will either lie on your stomach or sit with a pad behind your knee. Push against the pad, moving your knee up toward the ceiling or backward (depending on which position you’re in). “In other words, bend your knees,” Pariser says. But to avoid cramps in your hamstring muscles, don’t bend your knee so much that your heels are too close to your buttocks.
Im a skateboarder and a couple weeks ago i skated alot every day and my lefy hip was starting to get sore. But of course i couldnt resist skating so i kept skating and it got worse and worse to the point i couldnt really skate at all without my hip hurting but of course i would still mess around on the board doing tiny tricks but a couple days ago i was just skating around not really doing tricks and i slipped and kicked my leg out and REALLY hurt my hip and thought i tore a tendon or something and couldnt walk for two days, but its gotten alot better and i can walk fairly normal and i ice it everyday but whenever i stretch it its just a really sharp pain it doesnt feel like im stretching it. What do i do when all the stretch does is make a sharp pain? How do i strengthen my hip? And how long would it take to strengthen my hip to full strength again? Because i cant stand not being able to skate. Please reply so i can skate as soon as possible thank you
First and foremost, stop slouching. One of the most common causes of low back pain is poor sitting posture. The strain on the back while sitting in a slouched position can cause excessive pressure on the joints, muscles, and discs, causing pain. Learn to sit with correct posture and maintain that posture at all times to help decrease or eliminate your low back pain. Also be sure your workspace is set up properly at home and at work.
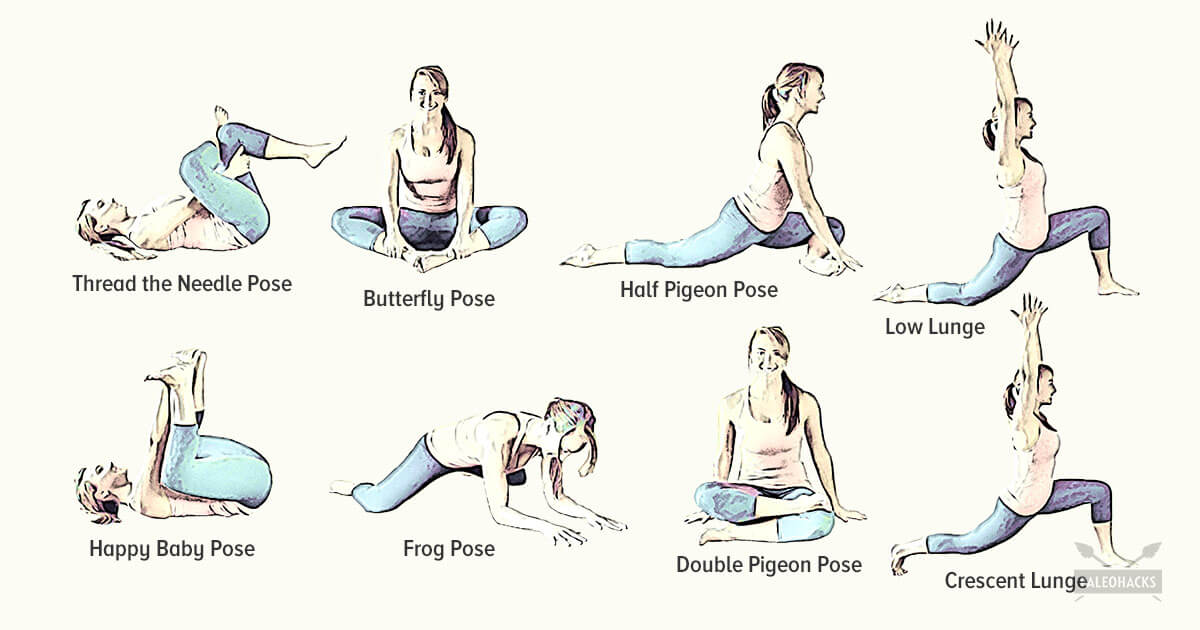
Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Place left ankle right below right knee, creating a “four” shape with left leg. Thread left arm through the opening you created with left leg and clasp hands behind right knee. Lift right foot off floor and pull right knee toward chest, flexing left foot. Hold for 30 seconds, then repeat on opposite side.
Kidneys — The kidneys are a matched pair. One painful kidney can cause back pain on one side or the other. Kidney pain can feel like back pain, and may occur on only one side. It is usually quite lateral, and just barely low enough to qualify as “low” back pain. However, when kidney stones descend through the ureters, they can cause (terrible) pain in the low back. Kidney stone pain is often so severe and develops so rapidly that it isn’t mistaken for a back pain problem.

Really a great content. Let me tell you first about hip flexor it is the engine through which our body moves. They control balance, our ability to sit, stand, twist, reach, bend, walk and step. One of my patient also suffering from same problem but due to lack of money he was unable to afford a treatment. So i recommend him a program to unlock hip flexor. If anyone wants they can check it out here ;- https://tinyurl.com/y8yaqs2s Report
Tight hip flexors can also make it harder for your glutes to activate—since they're opposing muscle groups, when one is really tight the other becomes lengthened. When a muscle is more lengthened than it should be, it takes away some of its ability to contract. When your glutes are in this compromised position, it can cause other muscles to do more work than they should, making your workouts less efficient and sometimes, increasing your risk of injury.

In this study, one patient with sciatica was sent for ten MRIs, which produced 49 distinct “findings,” 16 of them unique, none of which occurred in all ten reports. On average, each radiologist made about a dozen errors, seeing one or two things that weren’t there and missing about ten things that were. Yikes. Read a more detailed and informal description of this study.

I had physical therapy last year for lower back pain and these exercises were part of the regimen. I went 2 to 3 times a week and it actually worked, I was pain free. The therapist stated that as long as I incorporated these exercises into my daily life a few times a week, I would remain pain free. I did just that for a few months and she was right, I felt great. Unfortunately, I took being pain free for a few months for being “cured”, not so, pain is back, which is why I’m online looking for relief. After looking at this website, I realize, I already know what will work, these exercises duh, lol. As soon as I log off, I will hit the mat and as long as these exercises work as well as last year I am determined to do them on a regular basis (like the therapist suggested) and live pain free…at least in my back! 🙂

How to: Sit on the floor with knees bent so that your right shin is positioned in front of you, your left shin behind you and your left hip dropped all of the way to the floor (a). Inhale and press your left hip forward until you feel a stretch in the front of your hip (b). Exhale and press left hip back to the floor. That’s one rep (c). Complete six to eight reps, working each time to increase your range of motion. Repeat on the opposite side.
Pregnancy commonly leads to low back pain by mechanically stressing the lumbar spine (changing the normal lumbar curvature) and by the positioning of the baby inside of the abdomen. Additionally, the effects of the female hormone estrogen and the ligament-loosening hormone relaxin may contribute to loosening of the ligaments and structures of the back. Pelvic-tilt exercises and stretches are often recommended for relieving this pain. Women are also recommended to maintain physical conditioning during pregnancy according to their doctors' advice. Natural labor can also cause low back pain.

If you’re lucky, you won’t notice your hips are tight until you’re trying to do the Half Pigeon pose in your yoga class. But if you’re not so fortunate, your tight hips are making themselves known every time you so much as walk to the bathroom or sit on the couch—expressing themselves in the form of lower back pain and muscle stiffness. Tight hips can even shorten your stride, slowing your 5K goal time!
A complete medical history and physical exam can usually identify any serious conditions that may be causing the pain. During the exam, a health care provider will ask about the onset, site, and severity of the pain; duration of symptoms and any limitations in movement; and history of previous episodes or any health conditions that might be related to the pain. Along with a thorough back examination, neurologic tests are conducted to determine the cause of pain and appropriate treatment. The cause of chronic lower back pain is often difficult to determine even after a thorough examination.
Bridge: Still lying on your back with your feet flat on floor, lift your hips and torso off the floor into a bridge. Then interlace your hands underneath your hips and press your shoulders and upper arms into the floor, lifting your hips higher. Hold for 10 seconds. Lower yourself slowly back down, rolling down from the top of your spine to your tailbone. Repeat three times.
In the elderly, atherosclerosis can cause weakening of the wall of the large arterial blood vessel (aorta) in the abdomen. This weakening can lead to a bulging (aneurysm) of the aorta wall. While most aneurysms cause no symptoms, some cause a pulsating low back pain. Aneurysms of certain size, especially when enlarging over time, can require surgical repair with a grafting procedure to repair the abnormal portion of the artery.


